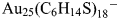Refine search
Actions for selected content:
106116 results in Materials Science
JMR volume 34 issue 16 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 16 / 28 August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2019, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
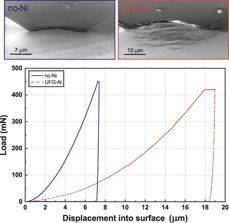
Determination of the true projected contact area by in situ indentation testing
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 16 / 28 August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2019, pp. 2859-2868
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Crystal structure of metolazone, C16H16ClN3O3S
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2019, pp. 361-367
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hydrothermal synthesis of Mg-substituted tricalcium phosphate nanocrystals
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2019, pp. 971-978
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
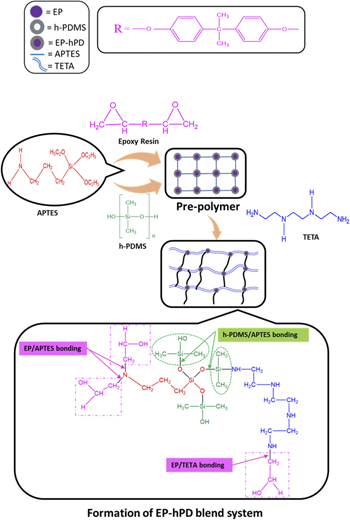
A facile preparation of epoxy-polydimethylsiloxane (EP-PDMS) polymer coatings for marine applications
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 16 / 28 August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2019, pp. 2881-2894
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Crystal structure of prednicarbate, C27H36O8
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2019, pp. 368-373
-
- Article
- Export citation
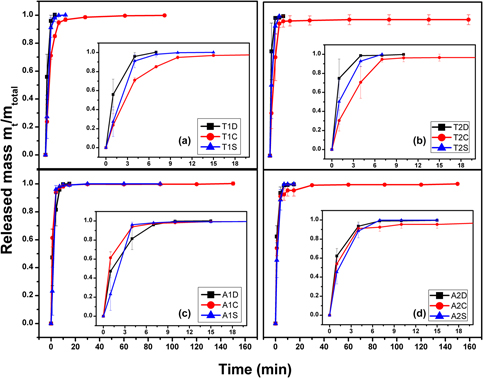
Nanotexturization of Ti-based implants in simulated body fluid: Influence of synthesis parameters on coating properties and kinetics of drug release
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 16 / 28 August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2019, pp. 2828-2836
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Investigations on electronic structure of YMnO3 by electron energy loss spectra and first-principle calculations
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2019, pp. 339-344
-
- Article
- Export citation
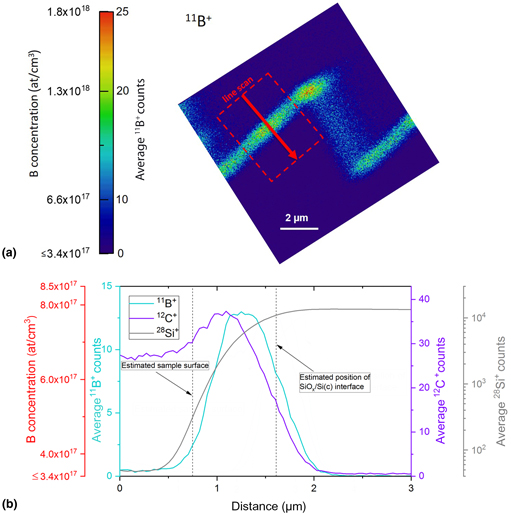
A method for quantitative nanoscale imaging of dopant distributions using secondary ion mass spectrometry: an application example in silicon photovoltaics
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2019, pp. 916-923
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
JMR volume 34 issue 16 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 16 / 28 August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 August 2019, pp. f1-f5
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
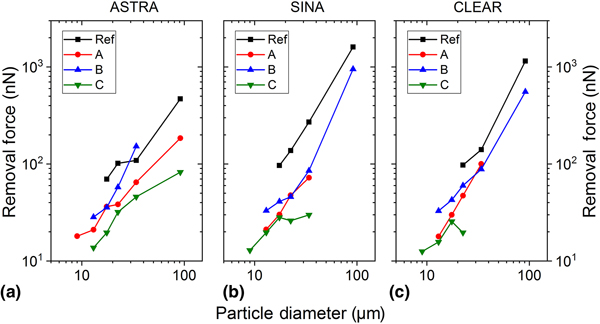
Particle size-dependent adhesion forces and wind removal efficiency of anti-soiling coatings on textured solar glasses
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2019, pp. 964-970
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
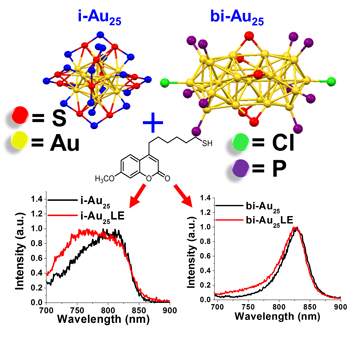
Variations in electronic states of coumarin hexanethiolate-labeled i-Au25 and bi-Au25 clusters
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2019, pp. 992-1000
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
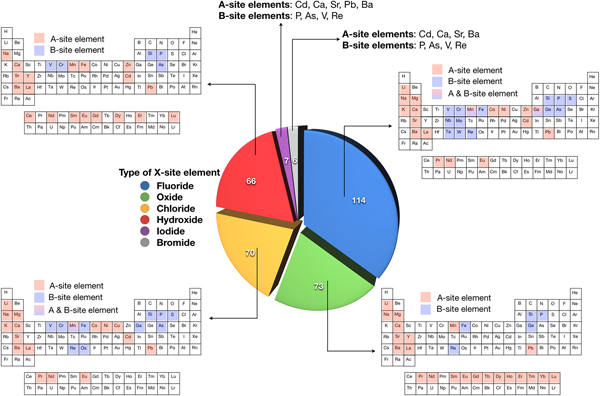
Prediction of new iodine-containing apatites using machine learning and density functional theory
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2019, pp. 882-890
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
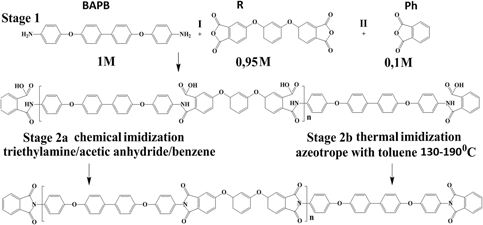
Development of new polyimide powder for selective laser sintering
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 16 / 28 August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2019, pp. 2895-2902
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Machine learning prediction of accurate atomization energies of organic molecules from low-fidelity quantum chemical calculations
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2019, pp. 891-899
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
High strength of ultrafine-grained Al–Mg films and the relevance of the modified Hall–Petch-type relationship
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2019, pp. 1111-1114
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
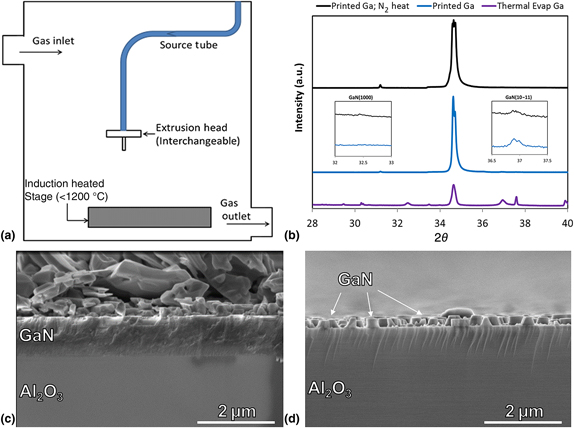
A pathway to compound semiconductor additive manufacturing
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2019, pp. 1001-1007
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Surface energetics of carbon nanotubes–based nanocomposites fabricated by microwave-assisted approach
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 19 / 14 October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2019, pp. 3361-3367
- Print publication:
- 14 October 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
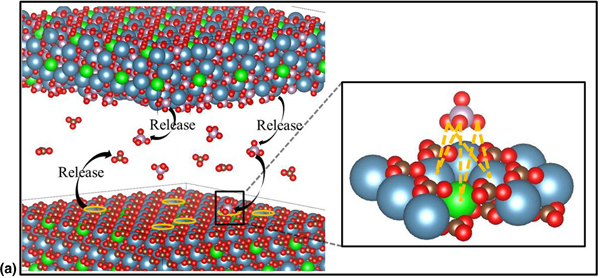
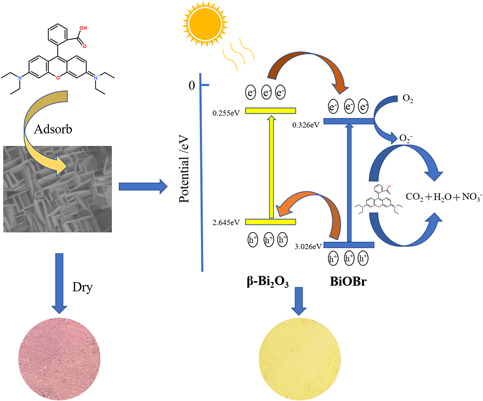
In situ synthesis of adsorptive β-Bi2O3/BiOBr photocatalyst with enhanced degradation efficiency
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2019, pp. 3450-3461
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of growth temperature on the key properties of aluminum-doped zinc oxide thin films prepared by atomic layer deposition
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2019, pp. 1105-1110
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation