Refine search
Actions for selected content:
106116 results in Materials Science
JMR volume 34 issue 15 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 15 / 14 August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2019, pp. f1-f5
- Print publication:
- 14 August 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
JMR volume 34 issue 15 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 15 / 14 August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2019, pp. b1-b5
- Print publication:
- 14 August 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
The effect of plastic on performance of activated carbon and study on adsorption of methylene blue
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 17 / 16 September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2019, pp. 3040-3049
- Print publication:
- 16 September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
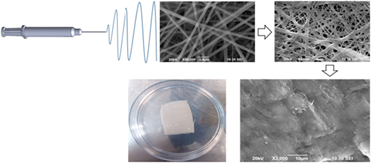
Collagen and elastin scaffold by electrospinning for skin tissue engineering applications
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 16 / 28 August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2019, pp. 2819-2827
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
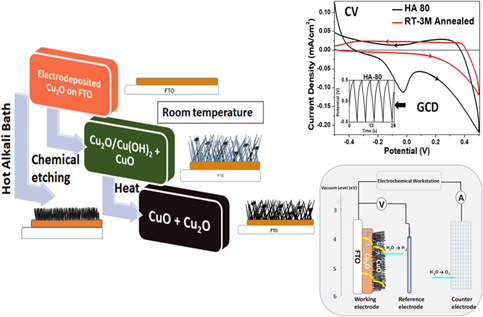
Low temperature–controlled synthesis of hierarchical Cu2O/Cu(OH)2/CuO nanostructures for energy applications
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 18 / 30 September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2019, pp. 3173-3185
- Print publication:
- 30 September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
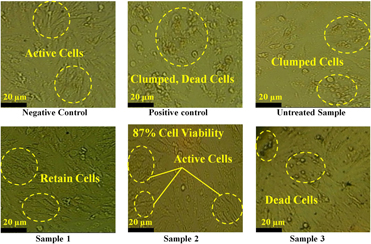
Potential of electrical discharge treatment to enhance the in vitro cytocompatibility and tribological performance of Co–Cr implant
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 16 / 28 August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2019, pp. 2837-2847
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Indium tin oxide nanowires as voltage self-stabilizing supercapacitor electrodes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 18 / 30 September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 August 2019, pp. 3195-3203
- Print publication:
- 30 September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
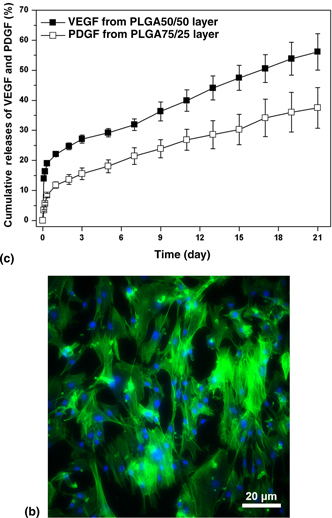
Dual release of VEGF and PDGF from emulsion electrospun bilayer scaffolds consisting of orthogonally aligned nanofibers for gastrointestinal tract regeneration
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 1098-1104
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Signal detection limit of a portable Raman spectrometer for the SERS detection of gunshot residue
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 948-955
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of temperature on the suppression of twinning in textured magnesium
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 1093-1097
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Utilizing additive manufacturing and gamified virtual simulation in the design of neuroprosthetics to improve pediatric outcomes
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 941-947
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Strong exciton–photon coupling in anthradithiophene microcavities: from isolated molecules to aggregates
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 956-963
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
PreDICT: a graphical user interface to the DICVOL14 indexing software program for powder diffraction data
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 233-241
-
- Article
- Export citation
Morphological effects on the third-order nonlinear optical response of polydiacetylene nanofibers
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 3 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 1087-1092
- Print publication:
- September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Ultrasonic welding of AZ31B magnesium alloy
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 44 / Issue 8 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 630-636
- Print publication:
- August 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Materials Research Science and Engineering Centers (MRSECs) provide collaboration and diversity in research and outreach
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 44 / Issue 8 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 658-660
- Print publication:
- August 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Influence of adherend properties on the strength of adhesively bonded joints
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 44 / Issue 8 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 625-629
- Print publication:
- August 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nondestructive evaluation of resistance spot-welded Al-steel joints
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 44 / Issue 8 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 619-624
- Print publication:
- August 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vaporizing foil actuator welding
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 44 / Issue 8 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, pp. 637-642
- Print publication:
- August 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
LOOK AGAIN
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 44 / Issue 8 / August 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 August 2019, p. 664
- Print publication:
- August 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation