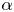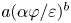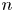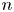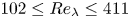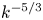Graphical abstract from Sarlin, W., Morize, C., Sauret, A. & Gondret, P. 2021 Nonlinear regimes of tsunami waves generated by a granular collapse. J. Fluid Mech. 919, R6. doi:10.1017/jfm.2021.400.
Contents
JFM Papers
Bounds on heat transport for convection driven by internal heating
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2021, A15
-
- Article
- Export citation
Stratification effect of air bubble on the shock wave from the collapse of cavitation bubble
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2021, A16
-
- Article
- Export citation
Suppression of turbulence and travelling waves in a vertical heated pipe
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2021, A17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Viscoelastic effects in circular edge waves
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2021, A18
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vortical–acoustic resonance in an acoustic resonator: Strouhal number variation, destabilization and stabilization
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2021, A19
-
- Article
- Export citation
Electrokinetic oscillatory flow and energy conversion of viscoelastic fluids in microchannels: a linear analysis
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2021, A20
-
- Article
- Export citation
Examining the inertial subrange with nanoscale cross-wire measurements of turbulent pipe flow at high Reynolds number near the centreline
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2021, A21
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hydrochemical interactions of phoretic particles: a regularized multipole framework
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2021, A22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Variational formulation of marine ice-sheet and subglacial-lake grounding-line dynamics
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2021, A23
-
- Article
- Export citation
Three-dimensional structural characteristics of flow separation induced by a forward-facing step in a turbulent channel flow
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2021, A24
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of non-uniform rheology on the motion of bubbles in a yield-stress fluid
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2021, A25
-
- Article
- Export citation
Transfer of internal energy fluctuation in compressible isotropic turbulence with vibrational non-equilibrium
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2021, A26
-
- Article
- Export citation
Vortex dynamics for flow around the slat cove at low Reynolds numbers
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2021, A27
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nonlinear interactions between an unstably stratified shear flow and a phase boundary
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2021, A28
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mathematical modelling of thermocapillary patterning in thin liquid film: an equilibrium study
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2021, A29
-
- Article
- Export citation
Viscid–inviscid interactions of pairwise bubbles in a turbulent channel flow and their implications for bubble clustering
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 May 2021, A30
-
- Article
- Export citation
The hydrodynamics of an active squirming particle inside of a porous container
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 May 2021, A31
-
- Article
- Export citation
Jet resonance in truncated ideally contoured nozzles
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2021, A32
-
- Article
- Export citation
Lower bounds on zonal enstrophy
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2021, A33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Numerical investigation of minimum drag profiles in laminar flow using deep learning surrogates
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 June 2021, A34
-
- Article
- Export citation