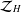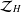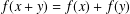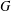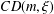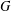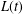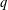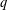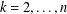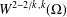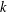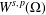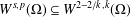Contents
Research Article
NEW GLOBAL LOGARITHMIC STABILITY RESULTS ON THE CAUCHY PROBLEM FOR ELLIPTIC EQUATIONS
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2019, pp. 141-145
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ON THE HARMONIC ZYGMUND SPACES
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 March 2020, pp. 466-476
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ON APPROXIMATELY ADDITIVE MAPPINGS IN 2-BANACH SPACES
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 August 2019, pp. 299-310
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ON A CLASS OF NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATIONS ON FINITE GRAPHS
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2020, pp. 477-487
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
LARGE DEVIATIONS FOR THE LONGEST GAP IN POISSON PROCESSES
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 October 2019, pp. 146-156
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ON THE GENERALISATION OF SIDEL’NIKOV’S THEOREM TO
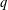 $q$-ARY LINEAR CODES
$q$-ARY LINEAR CODES
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2019, pp. 157-162
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
EMBEDDINGS OF FREE TOPOLOGICAL VECTOR SPACES
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 August 2019, pp. 311-324
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
THE FIRST COHOMOLOGY GROUP OF BANACH INVERSE SEMIGROUP ALGEBRAS WITH COEFFICIENTS IN
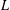 $L$-EMBEDDED BANACH BIMODULES
$L$-EMBEDDED BANACH BIMODULES
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. 488-495
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ON MODULATED TOPOLOGICAL VECTOR SPACES AND APPLICATIONS
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 July 2019, pp. 325-332
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Abstracts of Australasian PhD Theses
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION AND APPLICATION OF FRACTIONAL DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2019, pp. 163-165
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Research Article
THE DISTRIBUTIONAL
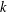 $k$-HESSIAN IN FRACTIONAL SOBOLEV SPACES
$k$-HESSIAN IN FRACTIONAL SOBOLEV SPACES
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2019, pp. 496-507
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Abstracts of Australasian PhD Theses
ISOGENIES OF ABELIAN VARIETIES IN CRYPTOGRAPHY
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 March 2020, pp. 508-509
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Research Article
ON ALMOST STABLE CMC HYPERSURFACES IN MANIFOLDS OF BOUNDED SECTIONAL CURVATURE
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 September 2019, pp. 333-338
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Abstracts of Australasian PhD Theses
COPULA-BASED STATISTICAL MODELLING OF SYNOPTIC-SCALE CLIMATE INDICES FOR QUANTIFYING AND MANAGING AGRICULTURAL RISKS IN AUSTRALIA
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 November 2019, pp. 166-169
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
THEORY AND STATISTICS OF LONG-RANGE DEPENDENT RANDOM PROCESSES
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2020, pp. 339-341
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ON BASE RADICAL THEORY IN FINITE SETTINGS
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2020, pp. 510-511
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
DEGREE BOUNDED GEOMETRIC SPANNING TREES WITH A BOTTLENECK OBJECTIVE FUNCTION
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2019, pp. 170-171
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
THE PERFORMANCE OF SOME STATISTICAL PROCEDURES USED IN CASE-CONTROL STUDIES AND METHYLOMICS
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2020, pp. 342-344
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
SIMPLICITY OF TWISTED C*-ALGEBRAS OF TOPOLOGICAL HIGHER-RANK GRAPHS
- Part of:
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2020, pp. 512-513
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
CANONICAL DUAL FINITE ELEMENT METHOD FOR SOLVING NONCONVEX MECHANICS AND TOPOLOGY OPTIMISATION PROBLEMS
-
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 November 2019, pp. 172-173
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation