Refine search
Actions for selected content:
106116 results in Materials Science
4 - Quantum Transport: General Concepts
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 92-119
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Preface to the First Edition
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp xiii-xvi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Index
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 457-462
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
5 - Klein Tunneling and Ballistic Transport in Graphene and Related Materials
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 120-144
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
10 - Ab Initio and Multiscale Quantum Transport in Graphene-Based Materials
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 293-353
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Appendix B - Electronic Structure Calculations: The Many-Body Perturbation Theory (MBPT)
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 373-378
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
6 - Quantum Transport in Disordered Graphene-Based Materials
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 145-209
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
1 - Introduction to Carbon-Based Nanostructures
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 1-10
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
3 - The New Family of Two-Dimensional Materials and van der Waals Heterostructures
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 70-91
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Appendix C - Green’s Functions and Ab Initio Quantum Transport in the Landauer–Büttiker Formalism
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 379-400
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
References
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 413-456
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Contents
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp v-x
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
9 - Quantum Transport beyond DC
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 278-292
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Appendix A - Electronic Structure Calculations: The Density Functional Theory (DFT)
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 354-372
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
8 - Spin-Related Phenomena
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 237-277
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Appendix D - Recursion Methods for Computing the Density of States (DOS) and Wavepacket Dynamics
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp 401-412
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Preface to the Second Edition
-
- Book:
- Introduction to Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
- Published online:
- 10 January 2020
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2020, pp xi-xii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Loss in acoustic metasurfaces: a blessing in disguise – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2020, p. 705
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
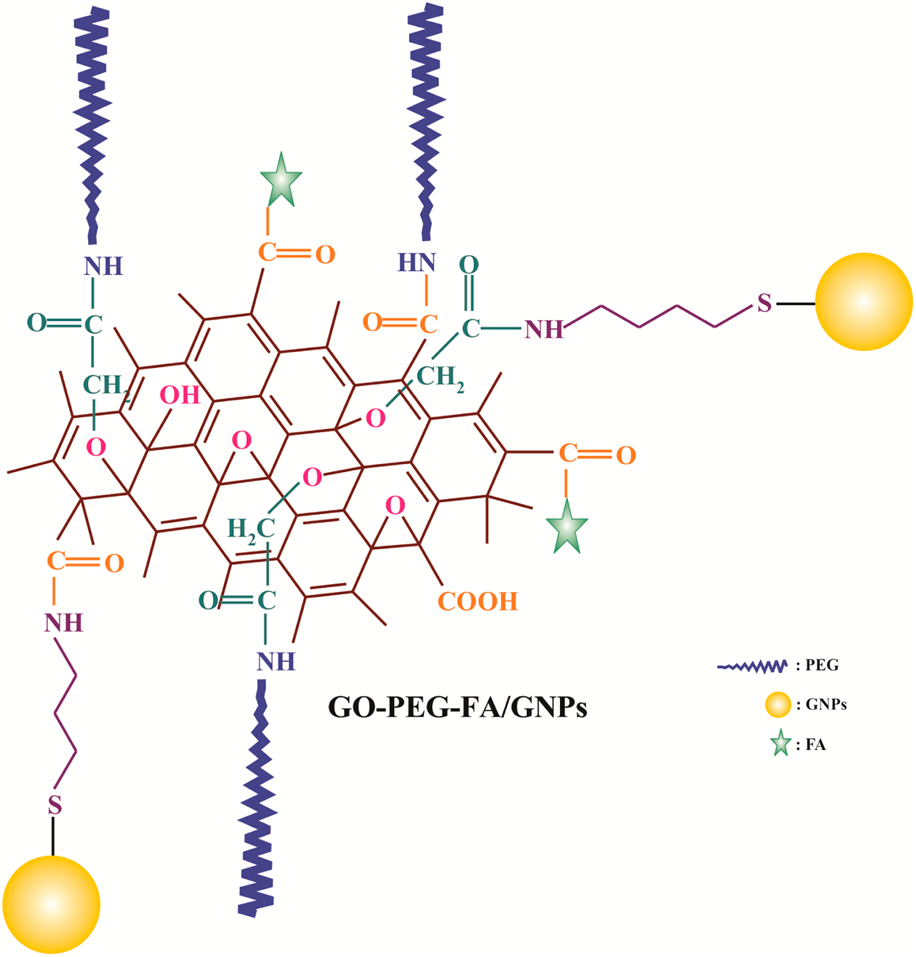
A de novo theranostic nanomedicine composed of PEGylated graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles for cancer therapy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2020, pp. 430-441
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hyaluronan-coated meta-organic framework loaded with cisplatin and oleanolic acid for synergetic chemotherapy of colorectal cancer
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 22 / 30 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2020, pp. 3106-3115
- Print publication:
- 30 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation