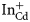Refine search
Actions for selected content:
106116 results in Materials Science
In situ XRPD study of the ambient-pressure synthesis of nonstoichiometric Ag3O from Ag–Ag2O thin films: Phase abundance, unit-cell parameters, and c/a as a function of temperature and time
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2020, pp. 247-261
-
- Article
- Export citation
Time-resolved in situ electrochemical atomic force microscopy imaging of the corrosion dynamics of AA2024-T3 using a new design of cell
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2020, pp. 1-15
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Probing surfaces and interfaces in complex oxide films via in situ X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2020, pp. 1-26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Probing structural and chemical evolution in (AlxGa1−x)2O3 using atom probe tomography: A review
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2020, pp. 1-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
BiOCl/TiO2 composite photocatalysts synthesized by the sol–gel method for enhanced visible-light catalytic activity toward methyl orange
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 22 / 30 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2020, pp. 3067-3078
- Print publication:
- 30 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Potential clinically significant life-threatening drug–drug interactions of lopinavir and ritonavir used in the treatment of COVID-19
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2020, e49
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Enhanced energy density and electric cycling reliability via MnO2 modification in sodium niobate-based relaxor dielectric capacitors
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 October 2020, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Structures of an extradiol catechol dioxygenase – C23O64, from 3-nitrotoluene degrading Diaphorobacter sp. strain DS2 in substrate-free, substrate-bound and substrate analog-bound states
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2020, e48
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Recent developments on fabrication of Al-matrix composites reinforced with quasicrystals: From metastable to conventional processing
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 October 2020, pp. 1-17
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Greater autism knowledge and contact with autistic people are independently associated with favourable attitudes towards autistic people
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, e46
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Nanoparticle Interactions and Molecular Relaxation in PLA/PBAT/Nanoclay Blends
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 October 2020, e47
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
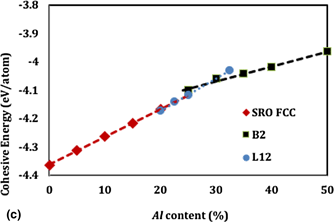
Model interatomic potentials for Fe–Ni–Cr–Co–Al high-entropy alloys
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 22 / 30 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2020, pp. 3031-3040
- Print publication:
- 30 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Governing role of the ratio of large platelet particles to ultrafine particles on dynamic and quasistatic compressive response and damage evolution in ice-templated alumina ceramics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 21 / 16 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2020, pp. 2870-2886
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
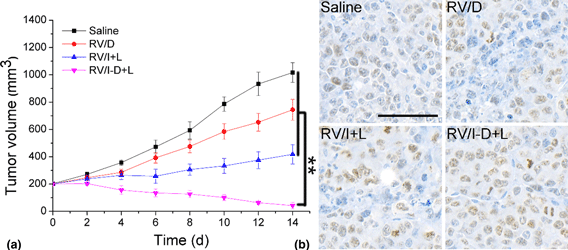
Red blood cells membrane vehicle co-delivering DOX and IR780 for effective prostate cancer therapy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 22 / 30 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 October 2020, pp. 3116-3123
- Print publication:
- 30 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hot deformation and softening response in boron-modified two-phase titanium aluminide Ti–48Al–2V–0.2B
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 October 2020, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Synthesis of the chiral stationary phase based on functionalized ZIF-8 with amylose carbamate
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 21 / 16 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 October 2020, pp. 2936-2949
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sensitivity estimation for calculated phase equilibria
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 October 2020, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Hydrogen passivation of defect levels in the annealed CdZnTe:In crystals
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 22 / 30 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 October 2020, pp. 3041-3047
- Print publication:
- 30 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Enhanced electrocaloric effect in compositional driven potassium sodium niobate-based relaxor ferroelectrics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 October 2020, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
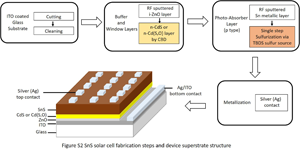
Tin sulfide (SnS) thin-film solar cells deposited by organic chemical vapor sulfurization based on CdS and high transmittance Cd(S,O) n-type layers with the superstrate device structure
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 October 2020, pp. 660-666
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation