Refine search
Actions for selected content:
106116 results in Materials Science
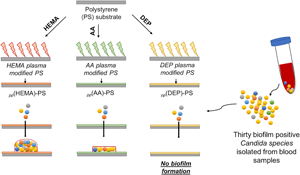
Prevention of Candida biofilm formation over polystyrene by plasma polymerization technique
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 October 2020, pp. 667-673
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of Rinsing Canned Foods on Bisphenol-A Exposure: The Hummus Experiment
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 October 2020, e45
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Introduction - Porous Metals: From Nano to Macro
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 19 / 14 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 October 2020, pp. 2529-2534
- Print publication:
- 14 October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
JMR volume 35 issue 19 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 19 / 14 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 October 2020, pp. f1-f4
- Print publication:
- 14 October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
JMR volume 35 issue 19 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 19 / 14 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 October 2020, pp. b1-b4
- Print publication:
- 14 October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Validation of XRD phase quantification using semi-synthetic data
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2020, pp. 262-275
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fabrication of anti-icing surface with halloysite spherical microcapsule
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 21 / 16 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 October 2020, pp. 2887-2896
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of the alloying element on the stacking fault energies of dilute Ir-based superalloys: A comprehensive first-principles study
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2020, pp. 2718-2725
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
First observations of Polar Mesospheric Echoes at both 31 MHz and 53.5 MHz over Svalbard (78.2°N 15.1°E)
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2020, e44
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Candida albicans isolated from denture-related stomatitis in elderly patients: Antifungal susceptibility and production of virulence attributes
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2020, e43
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
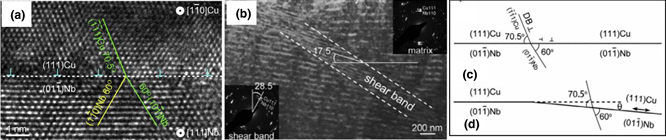
Interface effects on the properties of Cu–Nb nanolayered composites
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 October 2020, pp. 2684-2700
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
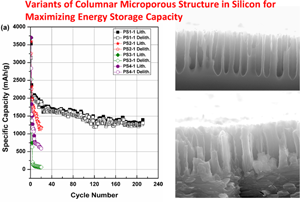
Large effect of structural variations in the columnar silicon electrode on energy storage capacity and electrode structural integrity in Li-ion cells
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 21 / 16 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 October 2020, pp. 2976-2988
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Preparation of superhydrophobic magnetic stearic acid polyurethane sponge for oil–water separation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 21 / 16 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 October 2020, pp. 2925-2935
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
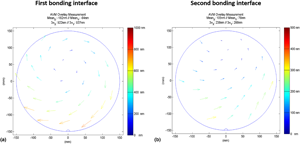
Three-dimensional hybrid bonding integration challenges and solutions toward multi-wafer stacking
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 October 2020, pp. 549-557
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Comparing the electromechanical properties of CaTiO3- and BaZrO3-modified Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3–SrTiO3 ceramics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 October 2020, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
- Export citation
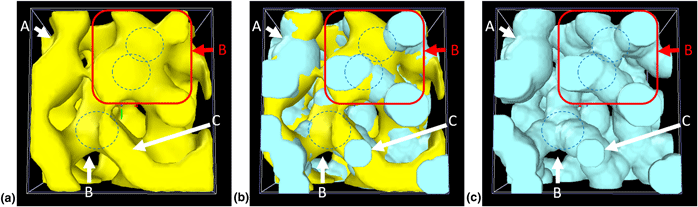
Comment to “Skeletonization-based beam finite element models for stochastic bicontinuous materials: Application to simulations of nanoporous gold” by C. Soyarslan et al. [J. Mater. Res. 33(20), 3371 (2018)]
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 October 2020, pp. 2831-2834
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Theoretical modeling of tunable vibrations of three-dimensional serpentine structures for simultaneous measurement of adherent cell mass and modulus
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 October 2020, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Exploring argon plasma effect on ferroelectric Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 thin film atomic layer deposition
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2020, pp. 1-8
-
- Article
- Export citation
Powder metallurgy of Al0.1CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 21 / 16 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2020, pp. 2835-2847
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of defect on thermal stability and photoluminescence in quenched Ho-doped 0.94Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3–0.06BaTiO3 lead-free ceramics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 October 2020, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation