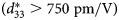Refine search
Actions for selected content:
106116 results in Materials Science
CAREER CENTRAL
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 45 / Issue 10 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2020, p. 871
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Creating meaningful slide presentations
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 45 / Issue 10 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2020, p. 870
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Research Highlights: Perovskites
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 45 / Issue 10 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2020, pp. 790-791
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
MRS Communications
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 45 / Issue 10 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2020, pp. 864-865
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Self-assembly for electronics
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 45 / Issue 10 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2020, pp. 807-814
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nanoparticles Induce Oxidative and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stresses: Antioxidant Therapeutic Defenses, Loutfy H. Madkour Springer, 2020 752 pages, $142 (hardcover) ISBN 9783030372965
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 45 / Issue 10 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2020, p. 868
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
LOOK AGAIN
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 45 / Issue 10 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2020, p. 872
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Electrochemical energy-storage material architecture built brick-by-brick
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 45 / Issue 10 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2020, pp. 792-793
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
EC announces actions to increase security and sustainability of Europe's raw materials supply
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 45 / Issue 10 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2020, p. 796
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
MRS authors recently elected to the US National Academy of Engineering
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin / Volume 45 / Issue 10 / October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 October 2020, p. 863
- Print publication:
- October 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
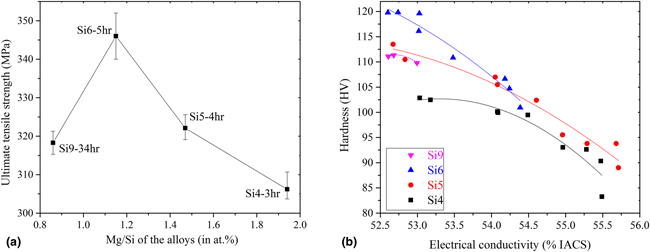
Optimization of mechanical properties and electrical conductivity in Al–Mg–Si 6201 alloys with different Mg/Si ratios
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2020, pp. 2765-2776
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
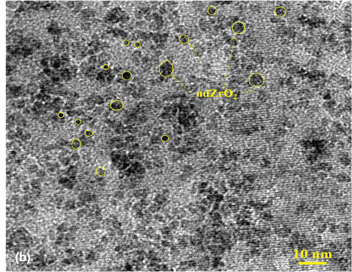
Biofunctionalized nanodot zirconia-based efficient biosensing platform for noninvasive oral cancer detection
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2020, pp. 652-659
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of the element ratio in the doping component on the properties of 0.975(0.8Bi1/2Na1/2TiO3–0.2Bi1/2K1/2TiO3)–0.025Bix/3Mgy/3Nbz/3O3 ceramics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2020, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
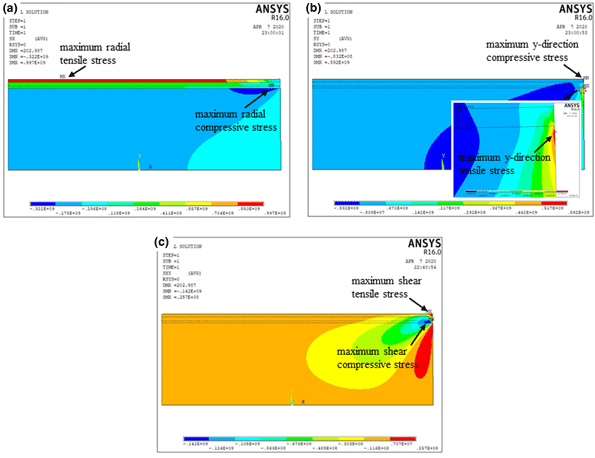
Thermal shock resistance of double-layer thermal barrier coatings
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2020, pp. 2808-2816
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
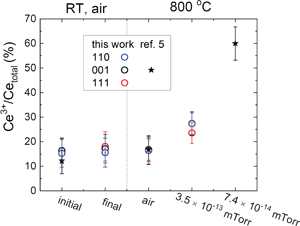
Insensitivity of the extent of surface reduction of ceria on termination: comparison of (001), (110), and (111) faces
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2020, pp. 636-641
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
In situ low-temperature hydrothermal synthesis of LiMn2O4 nanocomposites based on graphene oxide/carbon nanotubes hydrogel and its capacities – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2020, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
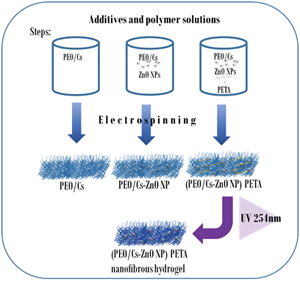
UV-initiated crosslinking of electrospun chitosan/poly(ethylene oxide) nanofibers doped with ZnO-nanoparticles: development of antibacterial nanofibrous hydrogel
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2020, pp. 642-651
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
JMR volume 35 issue 18 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 18 / 28 September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2020, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Helminth infection-induced carcinogenesis: spectrometric insights from the liver flukes, Opisthorchis and Fasciola
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2020, e40
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) reduces proliferative capacity and Brachyury levels in the chordoma cell line UCH-1
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2020, e39
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation