Article contents
Insensitivity of the extent of surface reduction of ceria on termination: comparison of (001), (110), and (111) faces
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 September 2020
Abstract
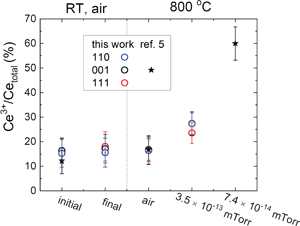
The enhanced reducibility of the surface of ceria relative to the bulk has long been established. Several studies also show that ceria nanoparticles with different facets exhibit different catalytic activities. Despite consensus that the activity is correlated with the surface Ce3+ concentration, experimental measurements of this concentration as a function of termination are lacking. Here, X-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy (XANES) is used to quantify the Ce3+ concentration in films with (001), (110), and (111) surface terminations under reaction relevant conditions. While an enhanced Ce3+ concentration is found at the surfaces, it is surprisingly insensitive to film orientation.
Information
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2020, published on behalf of Materials Research Society by Cambridge University Press
References
- 5
- Cited by


