Refine search
Actions for selected content:
106116 results in Materials Science
JMR volume 35 issue 18 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 18 / 28 September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 September 2020, pp. f1-f5
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Contact formation of C60 to thin films of formamidinium tin iodide
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 21 / 16 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 September 2020, pp. 2897-2904
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Low-temperature failure mechanism of [001] niobium micropillars under uniaxial tension
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2020, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
- Export citation
Accelerated microwave-assisted synthesis and in situ X-ray scattering of tungsten-substituted vanadium dioxide (V1−xWxO2)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2020, pp. 1-13
-
- Article
- Export citation
Energy conversion systems: Molecular architecture engineering of metal precursors and their applications to vapor phase and solution routes
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 21 / 16 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2020, pp. 2950-2966
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Improving photovoltaic performance of benzothiadiazole-based small molecules: A synergistic effect of non-covalent interaction and aryl terminal group
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 21 / 16 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2020, pp. 2967-2975
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
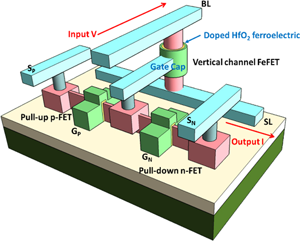
Ferroelectric devices and circuits for neuro-inspired computing
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2020, pp. 538-548
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
3D trajectories and diffusion of single ceria particles near a glass surface and their removal
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2020, pp. 1-10
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
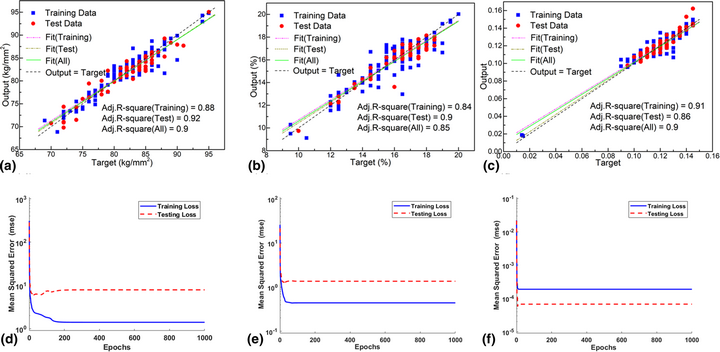
Predicting the optimum compositions of high-performance Cu–Zn alloys via machine learning
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2020, pp. 2709-2717
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
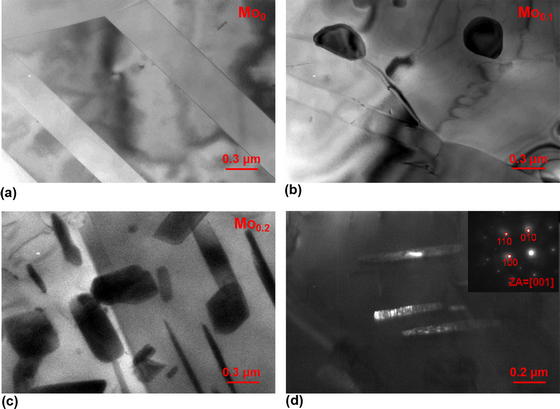
Effects of Mo-doping on the microstructure and mechanical properties of CoCrNi medium entropy alloy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2020, pp. 2726-2736
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of cerium addition on the corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of Mg–2Sr–1Zr Alloy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 22 / 30 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2020, pp. 3124-3135
- Print publication:
- 30 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Practicality of Tricone Bit Wear Condition Assessment
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 September 2020, e35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
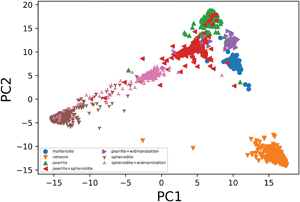
Microstructure representation learning using Siamese networks
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2020, pp. 613-619
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
A comparative study of the cooling-rate effect on rock strength reduction after microwave irradiation
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2020, e36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Response of macrobenthic communities to changes in water quality in a subtropical, microtidal estuary (Oso Bay, Texas)
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2020, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Evidence of Psychological Targeting but not Psychological Tailoring in Political Persuasion Around Brexit
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2020, e38
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
XPS and Electron Microscopy Study of Oxide-Scale Evolution on Ignition Resistant Mg-3Ca Alloy at Low and High Heating Rates
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 September 2020, e37
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Preface
-
- Book:
- Bioinspired Structures and Design
- Published online:
- 28 August 2020
- Print publication:
- 17 September 2020, pp xi-xii
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
COVID-19 impact on colleagues in the powder diffraction community
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 35 / Issue 3 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 September 2020, p. 155
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Copyright page
-
- Book:
- Bioinspired Structures and Design
- Published online:
- 28 August 2020
- Print publication:
- 17 September 2020, pp iv-iv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation