Refine search
Actions for selected content:
24 results
BINARY AND TERNARY CONGRUENCES INVOLVING INTERVALS AND SETS MODULO A PRIME
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 112 / Issue 2 / October 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2025, pp. 237-247
- Print publication:
- October 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
On Gaussian primes in sparse sets
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 161 / Issue 2 / February 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 June 2025, pp. 181-243
- Print publication:
- February 2025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
SHORT CHARACTER SUMS AND THEIR APPLICATIONS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 108 / Issue 2 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 July 2023, pp. 339-340
- Print publication:
- October 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
ON QUADRATIC FIELDS GENERATED BY POLYNOMIALS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 109 / Issue 3 / June 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 June 2023, pp. 476-485
- Print publication:
- June 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Smooth numbers with few nonzero binary digits
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 67 / Issue 1 / March 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 June 2023, pp. 74-89
- Print publication:
- March 2024
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mean value of real Dirichlet characters using a double Dirichlet series
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 66 / Issue 4 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 March 2023, pp. 1135-1151
- Print publication:
- December 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
GENERATORS OF FINITE FIELDS WITH PRESCRIBED TRACES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 112 / Issue 3 / June 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 May 2021, pp. 355-366
- Print publication:
- June 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Subproducts of small residue classes
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 65 / Issue 1 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 January 2021, pp. 1-8
- Print publication:
- March 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Pólya–Vinogradov inequality for short character sums
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 64 / Issue 4 / December 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 December 2020, pp. 906-910
- Print publication:
- December 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation
Character Sums Over Bohr Sets
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 58 / Issue 4 / 01 December 2015
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2018, pp. 774-786
- Print publication:
- 01 December 2015
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Sub-Weyl subconvexity for Dirichlet
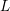 $L$-functions to prime power moduli
$L$-functions to prime power moduli
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 152 / Issue 4 / April 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 November 2015, pp. 825-875
- Print publication:
- April 2016
-
- Article
- Export citation
Groups generated by iterations of polynomials over finite fields
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 59 / Issue 1 / February 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 June 2015, pp. 235-245
-
- Article
- Export citation
Double Character Sums over Subgroups and Intervals
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 90 / Issue 3 / December 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 May 2014, pp. 376-390
- Print publication:
- December 2014
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
EXPONENTIAL AND CHARACTER SUMS WITH MERSENNE NUMBERS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 92 / Issue 1 / February 2012
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 April 2012, pp. 1-13
- Print publication:
- February 2012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On the Distribution of Irreducible Trinomials
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 54 / Issue 4 / 01 December 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2018, pp. 748-756
- Print publication:
- 01 December 2011
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
BOUNDS OF MULTIPLICATIVE CHARACTER SUMS WITH FERMAT QUOTIENTS OF PRIMES
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 83 / Issue 3 / June 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 February 2011, pp. 456-462
- Print publication:
- June 2011
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Subconvexity for a double Dirichlet series
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Compositio Mathematica / Volume 147 / Issue 2 / March 2011
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 September 2010, pp. 355-374
- Print publication:
- March 2011
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Bilinear character sums and sum-product problems on elliptic curves
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 53 / Issue 1 / February 2010
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 January 2010, pp. 1-12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
On quadratic fields generated by the Shanks sequence
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 52 / Issue 3 / October 2009
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 September 2009, pp. 719-729
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
ARITHMETIC AND GEOMETRIC PROGRESSIONS IN PRODUCT SETS OVER FINITE FIELDS
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 78 / Issue 3 / December 2008
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 December 2008, pp. 357-364
- Print publication:
- December 2008
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation























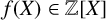
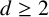
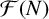
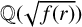
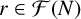
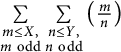


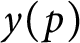
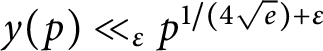
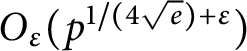
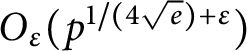
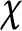
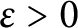
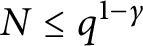
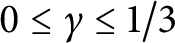
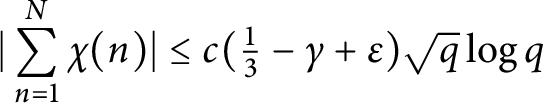

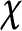
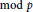
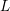
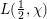
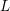
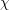
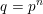
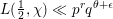

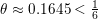
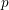
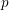
 of q elements, we consider a trajectory of the map
of q elements, we consider a trajectory of the map 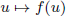 associated with a polynomial
associated with a polynomial  ]. Using bounds of character sums, under some mild condition on
]. Using bounds of character sums, under some mild condition on 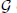 of
of  , improving the trivial lower bound
, improving the trivial lower bound 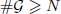 . Using a different technique, we also obtain a similar result for very small values of
. Using a different technique, we also obtain a similar result for very small values of 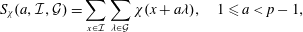
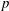
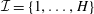
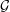
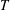
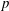
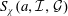
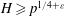
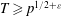
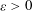
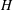
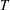
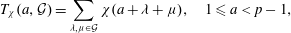
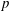
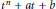
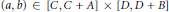
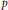
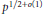
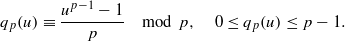
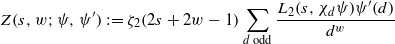
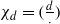 and the subscript 2 denotes the fact that the Euler factor at 2 has been removed. These double Dirichlet series can be extended to
and the subscript 2 denotes the fact that the Euler factor at 2 has been removed. These double Dirichlet series can be extended to 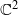 possessing a group of functional equations isomorphic to
possessing a group of functional equations isomorphic to 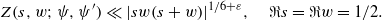
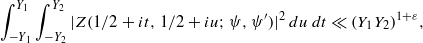
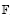
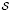 -unit equations as well as bounds for character sums to obtain a lower bound on the number of distinct fields among
-unit equations as well as bounds for character sums to obtain a lower bound on the number of distinct fields among 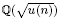 for
for 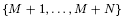 . Fields of this type include the Shanks fields and their generalizations.
. Fields of this type include the Shanks fields and their generalizations.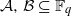 of elements of the finite field 𝔽
of elements of the finite field 𝔽