Refine search
Actions for selected content:
106116 results in Materials Science
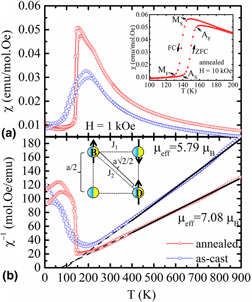
Thermal annealing influence on structural, magnetic, electronic, and mechanical properties of off-stoichiometric Ni40Cu10Mn35Ti15 all-d-metal Heusler alloy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 21 / 16 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 August 2020, pp. 3004-3011
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
A comparative study of calcium–magnesium–aluminum–silicon oxide mitigation in selected self-healing thermal barrier coating ceramics
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 17 / 14 September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 August 2020, pp. 2311-2320
- Print publication:
- 14 September 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Framing bullying as a health risk: Null effects on young adults’ support for anti-bullying policies
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 August 2020, e27
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Adsorption of water on epitaxial graphene
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 August 2020, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
Public awareness of tetralogy of Fallot after Jimmy Kimmel Live! television episode: A cross-sectional analysis
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2020, e26
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Cyclopentadithiophene polymers synthesised via Suzuki-Miyaura polymerisation of MIDA boronate esters
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2020, e28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Molten calcium–magnesium–aluminosilicate interactions with ytterbium disilicate environmental barrier coating
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 17 / 14 September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2020, pp. 2346-2357
- Print publication:
- 14 September 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
JMR volume 35 issue 15 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 15 / 14 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2020, pp. f1-f5
- Print publication:
- 14 August 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
JMR volume 35 issue 15 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 15 / 14 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2020, pp. b1-b3
- Print publication:
- 14 August 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Introduction
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 15 / 14 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 August 2020, p. 1899
- Print publication:
- 14 August 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Hydroxyapatite-dextran methacrylate core/shell hybrid nanocarriers for combinatorial drug therapy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 18 / 28 September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2020, pp. 2451-2465
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Microstructure and mechanical property of Cu/In–45Cu/Ni solder joints formed by transient liquid phase bonding
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 21 / 16 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 August 2020, pp. 2848-2858
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effect of poly(dimethylsiloxane) binder in a silica-based superhydrophobic coating on mechanical properties, surface roughness, and wettability
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 3 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 August 2020, pp. 512-518
- Print publication:
- September 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Glucose-responsive shape-memory cryogels
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 18 / 28 September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 August 2020, pp. 2396-2404
- Print publication:
- 28 September 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Electrochemical detection of natural organic matter (humic acid) and splitting of hydrogen peroxide on a micropore 3D catalytic polysulfone–copper oxide nanocomposite surface
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 3 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 August 2020, pp. 519-527
- Print publication:
- September 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Borospherene molecular junction-based sensor for detecting radium and radon in water
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 22 / 30 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 August 2020, pp. 3048-3057
- Print publication:
- 30 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
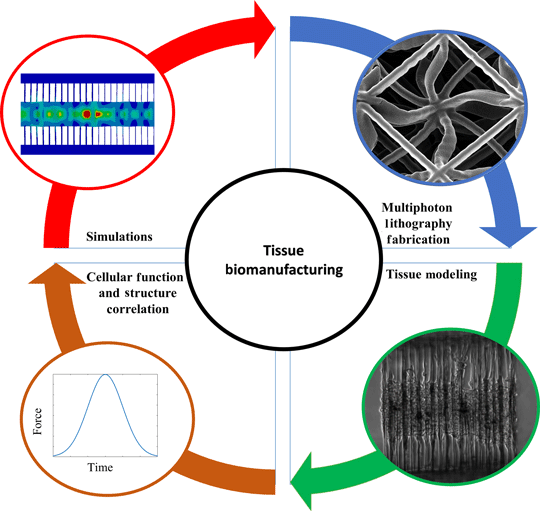
Architected mechanical designs in tissue engineering
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 3 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 August 2020, pp. 379-390
- Print publication:
- September 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Blend-based fibers produced via centrifugal spinning and electrospinning processes: Physical and rheological properties
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 21 / 16 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 August 2020, pp. 2905-2916
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Picturing science and engineering
-
- Journal:
- MRS Bulletin , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 August 2020, pp. 1-5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
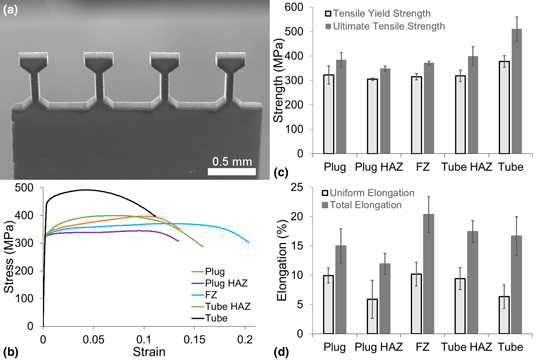
Sizing up mechanical testing: Comparison of microscale and mesoscale mechanical testing techniques on a FeCrAl welded tube
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 August 2020, pp. 2817-2830
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation