Refine search
Actions for selected content:
106116 results in Materials Science
Interface passivation strategy improves the efficiency and stability of organic–inorganic hybrid metal halide perovskite solar cells
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 16 / 28 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2020, pp. 2166-2189
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
JMR volume 35 issue 16 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 16 / 28 August 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 August 2020, pp. f1-f5
- Print publication:
- 28 August 2020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Infection to Recovery; COVID-19 in Pakistan and its Implications
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2020, e32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Computational approach to identify potential antileishmanial activity of reported inhibitor, E5700 and two natural alkaloids against Leishmania donovani Squalene Synthase
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2020, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Use of navigation GPSs in small topographical surveying – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 August 2020, e33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
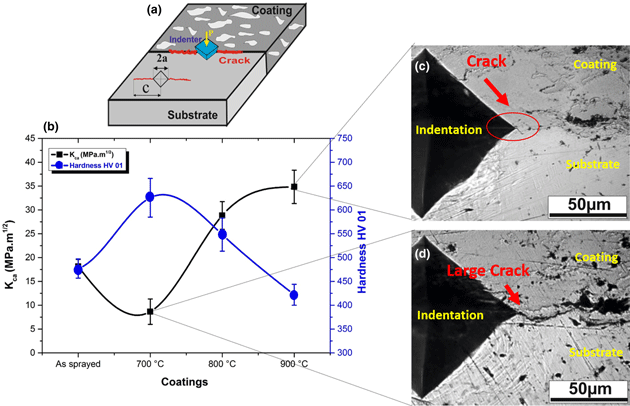
Effect of annealing temperature on the microstructure evolution, mechanical and wear behavior of NiCr–WC–Co HVOF-sprayed coatings
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 August 2020, pp. 2798-2807
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
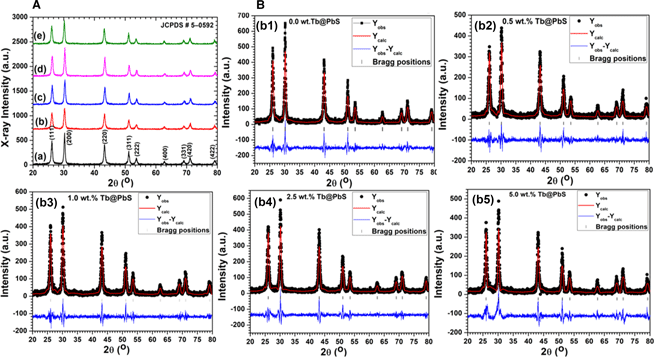
A novel terbium doping effect on physical properties of lead sulfide nanostructures: A facile synthesis and characterization
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 August 2020, pp. 2664-2675
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nanostructure morphology influences in electrical properties of titanium dioxide thin films
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 21 / 16 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 August 2020, pp. 3012-3020
- Print publication:
- 16 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
X-ray powder diffraction data for estra-4,9-diene-3,17-dione, C18H22O2
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2020, pp. 282-285
-
- Article
- Export citation
Crystal structure of ceftriaxone sodium hemiheptahydrate, C18H16N8O7S3Na2(H2O)3.5
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 35 / Issue 3 / September 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2020, pp. 206-212
-
- Article
- Export citation
An investigation into the temperature phase transitions of synthesized lithium titanate materials doped with Al, Co, Ni and Mg by in situ powder X-ray diffraction
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 35 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 August 2020, pp. 233-246
-
- Article
- Export citation
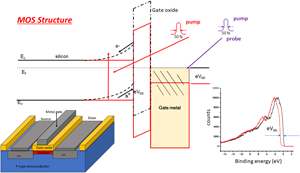
Electronic structure of technologically important interfaces and heterostructures
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2020, pp. 529-537
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nitrite sensor based on room temperature ionic liquid functionalized α-zirconium phosphate modified glassy carbon electrode
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 22 / 30 November 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2020, pp. 3058-3066
- Print publication:
- 30 November 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Effects of inundation duration on southeastern Louisiana oyster reefs
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2020, e30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
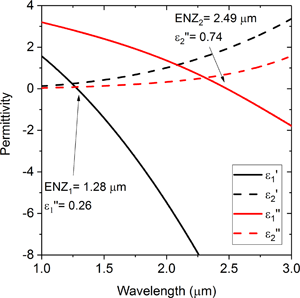
Tunable indium tin oxide for metamaterial perfect absorbers and nonlinear devices
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 10 / Issue 4 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2020, pp. 573-578
- Print publication:
- December 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
X-ray computed microtomography for the structural analysis of jewelry from the Museum “Royal Tombs of Sipán”
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 35 / Issue S1 / December 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 August 2020, pp. S38-S42
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nanoporous metal–polymer composite membranes for organics separations and catalysis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 35 / Issue 19 / 14 October 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 August 2020, pp. 2629-2642
- Print publication:
- 14 October 2020
-
- Article
- Export citation
Simplifying the Measurement of Attitudes towards Autistic People
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 August 2020, e29
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A Computational Model for Estimating the Progression of COVID-19 Cases in the US West and East Coast Population Regions
-
- Journal:
- Experimental Results / Volume 1 / 2020
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 August 2020, e41
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mechanical phase mapping of the Taza meteorite using correlated high-speed nanoindentation and EDX
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 August 2020, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation