Refine search
Actions for selected content:
106116 results in Materials Science
On the numerical modeling of nucleation and growth of microstructurally short cracks in polycrystals under cyclic loading
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 September 2019, pp. 3523-3534
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
PDJ volume 34 issue S1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 34 / Issue S1 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. b1-b5
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Proceedings of the 16th European powder diffraction conference
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 34 / Issue S1 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, p. S1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Use of surface photo-reactive nanometal printing for polymer thin-film transistors: contact resistance and short-channel effects
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 4 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. 1181-1185
- Print publication:
- December 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Anisotropic thermal conductivity in direction-specific black phosphorus nanoflakes
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 4 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. 1311-1316
- Print publication:
- December 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Building advanced materials via particle aggregation and molecular self-assembly
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 17 / 16 September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. 2911-2913
- Print publication:
- 16 September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Investigation on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al–5.50Zn–2.35Mg–1.36Cu alloy fabricated by hot extrusion process
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 18 / 30 September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. 3151-3162
- Print publication:
- 30 September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Redox-active polymers (redoxmers) for electrochemical energy storage
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 4 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. 1151-1167
- Print publication:
- December 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
The structure and thermochemistry of K2CO3–MgCO3 glass
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 19 / 14 October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. 3377-3388
- Print publication:
- 14 October 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
JMR volume 34 issue 17 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 17 / 16 September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. b1-b4
- Print publication:
- 16 September 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Microstructures and tensile properties of off-stoichiometric Ni3Al–Ni3V pseudo-binary alloys
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 18 / 30 September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. 3061-3070
- Print publication:
- 30 September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Multigeneration solution-processed method for silver nanotriangles exhibiting narrow linewidth (∼170 nm) absorption in near-infrared
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. 3420-3427
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mechanical, tribological, and electrochemical behavior of hybrid aluminum matrix composite containing boron carbide (B4C) and graphene nanoplatelets
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 18 / 30 September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. 3116-3129
- Print publication:
- 30 September 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
PDJ volume 34 issue S1 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Powder Diffraction / Volume 34 / Issue S1 / September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. f1-f6
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Preparation of multicolored carbon quantum dots using HNO3/HClO4 oxidation of graphitized carbon
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. 3428-3438
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
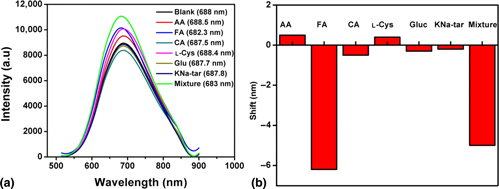
Selective detection of folic acid in the midst of other biomolecules using water-soluble AgInS2 quantum dots
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 4 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. 1306-1310
- Print publication:
- December 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
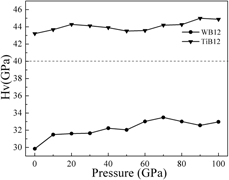
First-principles study of structure and mechanical properties of TMB12(TM = W and Ti) superhard material under pressure
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. 3554-3562
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
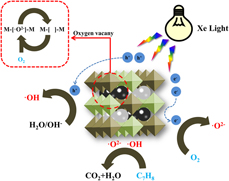
Mesoporous double-perovskite LaAMnNiO6 (A = La, Pr, Sm) photothermal synergistic degradation of gaseous toluene
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 20 / 28 October 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. 3439-3449
- Print publication:
- 28 October 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
JMR volume 34 issue 17 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 17 / 16 September 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 September 2019, pp. f1-f5
- Print publication:
- 16 September 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Preparation of graphene oxide-reinforced calcium phosphate/calcium sulfate/methylcellulose-based injectable bone substitutes
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 4 / December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 September 2019, pp. 1174-1180
- Print publication:
- December 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation