Refine search
Actions for selected content:
106116 results in Materials Science
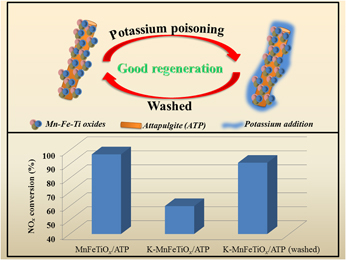
MnFeTiOx/attapulgite catalysts with excellent potassium resistance for SCR of NOx with NH3 at low temperatures
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 7 / 15 April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2019, pp. 1188-1199
- Print publication:
- 15 April 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
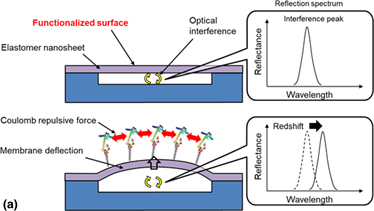
Elastomer-based MEMS optical interferometric transducers for highly sensitive surface stress sensing for biomolecular detection
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2019, pp. 381-389
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
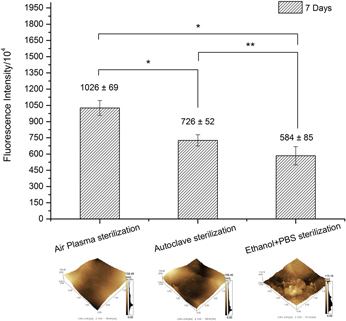
Effect of sterilization processes on nanostructured Ti6Al4V surfaces obtained by electropolishing
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 8 / 29 April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 February 2019, pp. 1439-1446
- Print publication:
- 29 April 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
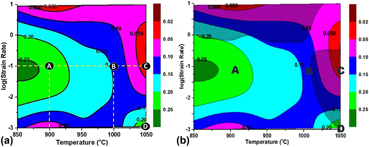
Hot deformation behavior of the high-entropy alloy CoCuFeMnNi
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 5 / 14 March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2019, pp. 744-755
- Print publication:
- 14 March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
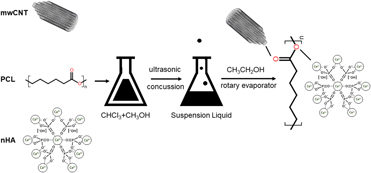
In vitro evaluation of a novel multiwalled carbon nanotube/nanohydroxyapatite/polycaprolactone composite for bone tissue engineering
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2019, pp. 532-544
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
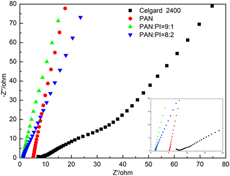
Study on preparation of polyacrylonitrile/polyimide composite lithium-ion battery separator by electrospinning
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2019, pp. 642-651
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
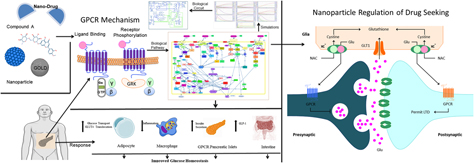
G-protein-coupled receptors function as logic gates for nanoparticle binding using systems and synthetic biology approach
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 11 / 14 June 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2019, pp. 1854-1867
- Print publication:
- 14 June 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
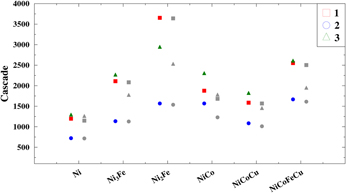
Radiation stability of nanocrystalline single-phase multicomponent alloys
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 5 / 14 March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2019, pp. 854-866
- Print publication:
- 14 March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Electrodeposition of Co–Ni–P/graphene oxide composite coating with enhanced wear and corrosion resistance
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 10 / 28 May 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 February 2019, pp. 1726-1733
- Print publication:
- 28 May 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
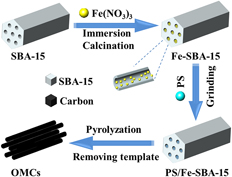
Conversion of waste plastic into ordered mesoporous carbon for electrochemical applications
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 February 2019, pp. 941-949
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
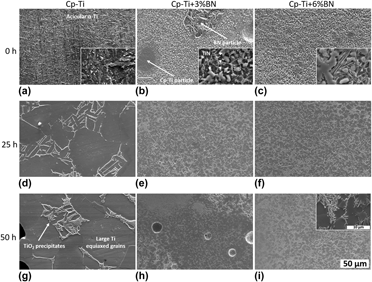
Influence of boron nitride on reinforcement to improve high temperature oxidation resistance of titanium
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 7 / 15 April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 February 2019, pp. 1279-1289
- Print publication:
- 15 April 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
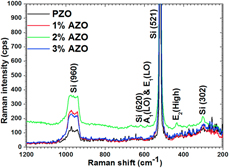
A structural, morphological, linear, and nonlinear optical spectroscopic studies of nanostructured Al-doped ZnO thin films: An effect of Al concentrations
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 8 / 29 April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 February 2019, pp. 1309-1317
- Print publication:
- 29 April 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Alloying behavior and thermal stability of mechanically alloyed nano AlCoCrFeNiTi high-entropy alloy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 5 / 14 March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2019, pp. 787-795
- Print publication:
- 14 March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Microstructure and corrosion resistance of Ni–P gradient coating/stannate conversion film on magnesium alloy
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 6 / 28 March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2019, pp. 1064-1072
- Print publication:
- 28 March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Nearly full-density pressureless sintering of AlCoCrFeNi-based high-entropy alloy powders
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 5 / 14 March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 February 2019, pp. 777-786
- Print publication:
- 14 March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Review of surface water interactions with metal oxide nanoparticles
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / 14 February 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2019, pp. 416-427
- Print publication:
- 14 February 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
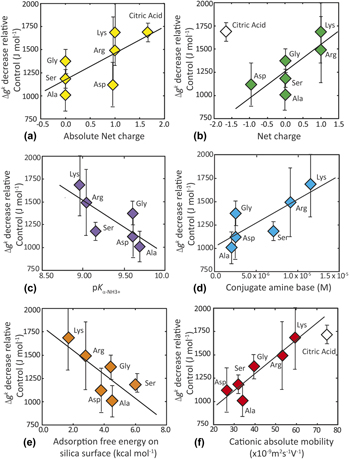
Systematic dependence of kinetic and thermodynamic barriers to homogeneous silica nucleation on NaCl and amino acids
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / 14 February 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2019, pp. 442-455
- Print publication:
- 14 February 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Introduction
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / 14 February 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2019, pp. 357-358
- Print publication:
- 14 February 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
JMR volume 34 issue 3 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / 14 February 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2019, pp. f1-f5
- Print publication:
- 14 February 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
JMR volume 34 issue 3 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 3 / 14 February 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 February 2019, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- 14 February 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation