Article contents
Elastomer-based MEMS optical interferometric transducers for highly sensitive surface stress sensing for biomolecular detection
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 February 2019
Abstract
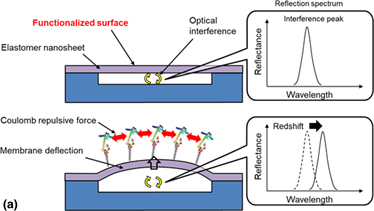
We developed a microelectromechanical-system optical interferometer based on an elastomer nanosheet using a polystyrene-polybutadiene-polystyrene (SBS) triblock copolymer for a suspended membrane as a way to improve the stress sensitivity for surface stress detection. The elastomeric SBS nanosheet provides a low Young's modulus of 28 ± 11 MPa, a large elastic strain of 24 ± 12%, and high adhesiveness, of which the surface charge and mechanical property are tunable by layer-by-layer (LbL) deposition of polysaccharides. A freestanding SBS nanosheet can be formed above a microcavity using a dry transfer technique without applying vacuum or high-temperature processes. The maximum deflection associated with molecular adsorption increased by sevenfold compared with a parylene-C-based optical interferometric transducer.
Information
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2019
Footnotes
This author was an editor of this journal during the review and decision stage. For the JMR policy on review and publication of manuscripts authored by editors, please refer to http://www.mrs.org/editor-manuscripts/.
References
- 9
- Cited by

