Refine search
Actions for selected content:
212053 results in Engineering
Modified design of sub-reflector with dielectric cylindrical keeper to enhance gain in axially displaced ellipse reflector with dual polarization
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 17 / Issue 4 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, pp. 613-619
-
- Article
- Export citation
How large-scale flow structures affect particle transport in wall turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, A23
-
- Article
- Export citation
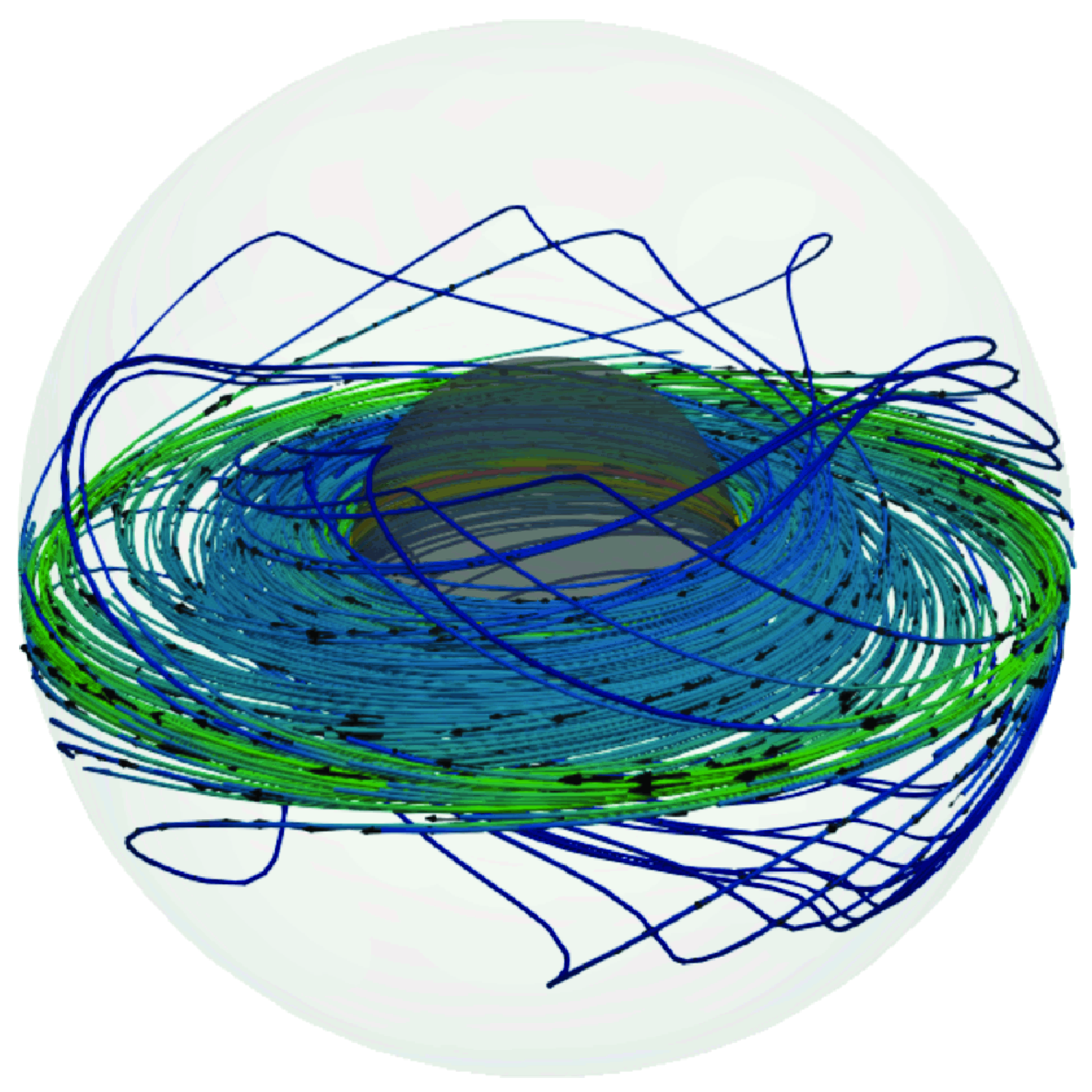
Electromagnetically driven magnetized spherical Couette flow
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, A25
-
- Article
- Export citation
Swimming and mixing of an ellipsoidal squirmer in a viscoplastic fluid
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, A12
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Revisiting the hydrodynamic modulation of short surface waves by longer waves
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, A20
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Streaming and diffusion in the cochlea
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 July 2025, A15
-
- Article
- Export citation
A soft 3-DOF interaction force measurement system for estimating the biomechanical effects of a soft wearable robot on the human joint
-
- Journal:
- Wearable Technologies / Volume 6 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2025, e32
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Mechanisms underlying the generation and generalisation of the surface layer – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1014 / 10 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2025, E3
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ka-band thin-film compact cascaded reflective-type phase shifter exploiting CVD-grown-graphene diode
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2025, pp. 1-9
-
- Article
- Export citation
Wind-farm wake recovery mechanisms in conventionally neutral boundary layers
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2025, A5
-
- Article
- Export citation
The effect of gravity on bubble–particle collisions in turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2025, A4
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
High-precision coupled method for interior ballistics of gun with self-sealing band
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 129 / Issue 1341 / November 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 15 July 2025, pp. 3004-3029
-
- Article
- Export citation
A 0.82 μm, 105 W diode-pumped thulium-doped all-silica-fiber laser
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- High Power Laser Science and Engineering / Volume 13 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2025, e58
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multilayer signal-interference fourth-order high-selectivity dual-band bandpass filter with multiple transmission zeros
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 17 / Issue 4 / May 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2025, pp. 595-602
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Attenuation mechanism of wall-bounded turbulence by heavy finite-size particles
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1014 / 10 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2025, A30
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A novel Kadomtsev–Petviashvili type model for nonlinear internal waves with horizontally two-dimensional shear currents and Earth’s rotation
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2025, A3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Open energy services: forecasting and optimization as a service for energy management applications at scale
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Data-Centric Engineering / Volume 6 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2025, e35
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Understanding the perspectives of older adults and physiotherapists on home-based lower-limb exoskeletons
-
- Journal:
- Wearable Technologies / Volume 6 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2025, e31
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Numerical investigation of magnetic pole angle on the aerodynamic heating and force properties of hypersonic magnetohydrodynamic in two-dimensional axisymmetric geometry
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 129 / Issue 1341 / November 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2025, pp. 3305-3326
-
- Article
- Export citation
Inter-scale energy transfer and interaction in a turbulent channel flow with randomly distributed wall roughness
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1015 / 25 July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 14 July 2025, A2
-
- Article
- Export citation