No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Inter-scale energy transfer and interaction in a turbulent channel flow with randomly distributed wall roughness
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 July 2025
Abstract
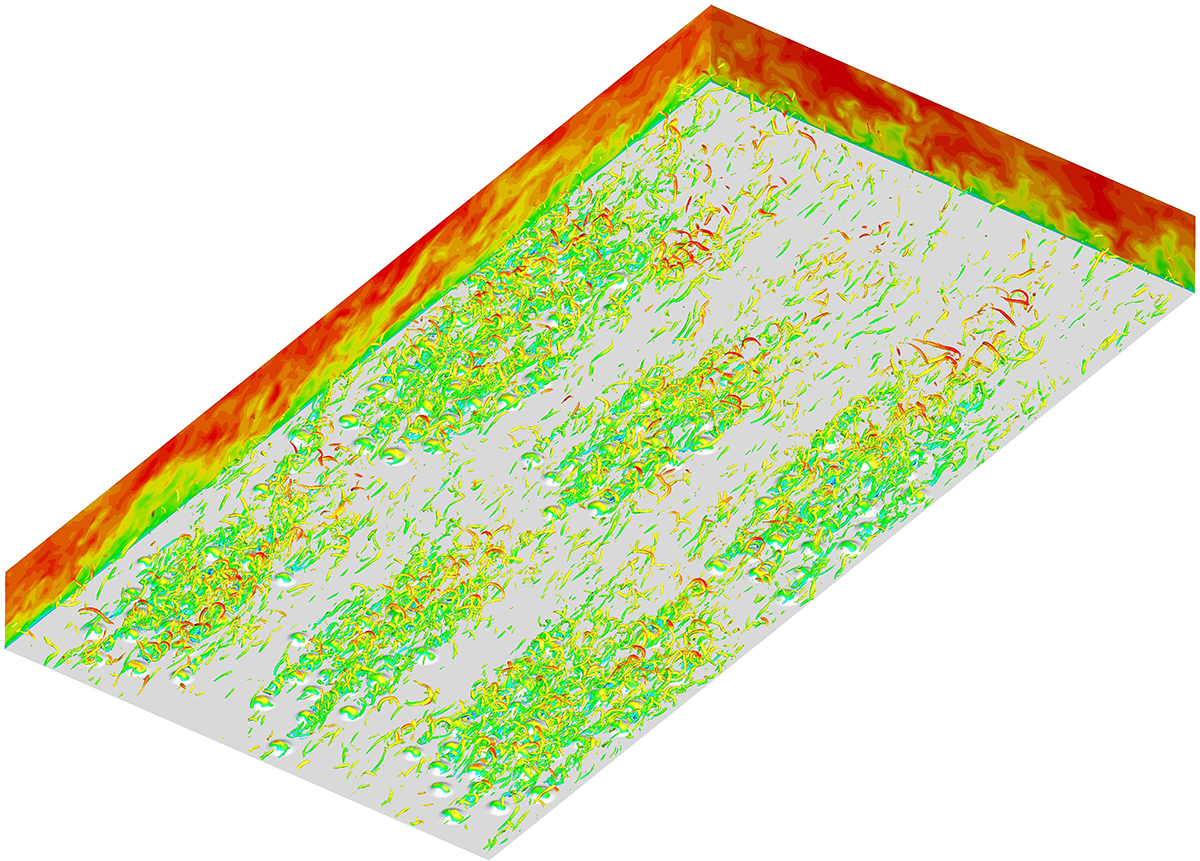
Direct numerical simulations are performed to explore the impact of surface roughness on inter-scale energy transfer and interaction in a turbulent open-channel flow over differently arranged rough walls. With friction Reynolds number approximately 540, six distinct configurations of roughness arrangements are examined. The results show that the clustered roughness arrangements yield notable changes in large-scale secondary-flow structures, which manifest in the profiles of dispersive stresses, predominantly near the roughness elements. They are marked by the presence of spanwise alternating high-momentum pathways and low-momentum pathways. From the outer peak in the spanwise energy spectra, the size and intensity of turbulent secondary flows are shown to be related to the spanwise spacing of the roughness heterogeneity. The emergence of turbulent secondary flows serves to suppress the original large-scale structures in the outer region of smooth-wall turbulence, paving the way for the development of new turbulent structures at the second harmonic scale. Furthermore, the spanwise triadic interaction analysis reveals the mutual energy exchange between the secondary harmonic scale and the secondary-flow scale. These findings elucidate the underlying mechanisms behind the attenuation of large-scale structures in the outer region influenced by roughness, offering new insights into the dynamic interplay of scale interactions in rough-wall turbulence.
JFM classification
Information
- Type
- JFM Papers
- Information
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2025. Published by Cambridge University Press


