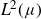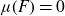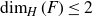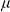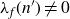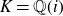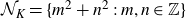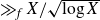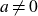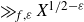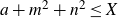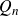Refine search
Actions for selected content:
26204 results in Theoretical Physics and Mathematical Physics
B - Appendix B Compendium of Sigma Matrix and Fierz Identities
- from Part V - The Appendices
-
- Book:
- From Spinors to Supersymmetry
- Published online:
- 06 July 2023
- Print publication:
- 08 June 2023, pp 807-818
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
13 - The Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model
- from Part III - Realistic Supersymmetric Models
-
- Book:
- From Spinors to Supersymmetry
- Published online:
- 06 July 2023
- Print publication:
- 08 June 2023, pp 493-547
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Bibliography
-
- Book:
- From Spinors to Supersymmetry
- Published online:
- 06 July 2023
- Print publication:
- 08 June 2023, pp 985-991
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part III - Realistic Supersymmetric Models
-
- Book:
- From Spinors to Supersymmetry
- Published online:
- 06 July 2023
- Print publication:
- 08 June 2023, pp 491-664
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
H - Appendix H Lie Group and Algebra Techniques for Gauge Theories
- from Part V - The Appendices
-
- Book:
- From Spinors to Supersymmetry
- Published online:
- 06 July 2023
- Print publication:
- 08 June 2023, pp 901-946
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
A - Appendix A Notations and Conventions
- from Part V - The Appendices
-
- Book:
- From Spinors to Supersymmetry
- Published online:
- 06 July 2023
- Print publication:
- 08 June 2023, pp 791-806
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
14 - Realizations of Supersymmetry Breaking
- from Part III - Realistic Supersymmetric Models
-
- Book:
- From Spinors to Supersymmetry
- Published online:
- 06 July 2023
- Print publication:
- 08 June 2023, pp 548-574
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
11 - Radiative Corrections in Supersymmetry
- from Part II - Constructing Supersymmetric Theories
-
- Book:
- From Spinors to Supersymmetry
- Published online:
- 06 July 2023
- Print publication:
- 08 June 2023, pp 434-478
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Index
-
- Book:
- From Spinors to Supersymmetry
- Published online:
- 06 July 2023
- Print publication:
- 08 June 2023, pp 999-1010
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
1 - Two-Component Formalism for Spin-1/2 Fermions
- from Part I - Spin-1/2 Fermions in Quantum Field Theory, the Standard Model, and Beyond
-
- Book:
- From Spinors to Supersymmetry
- Published online:
- 06 July 2023
- Print publication:
- 08 June 2023, pp 3-51
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
I - Appendix I Interaction Vertices of the SM and Its Seesaw Extension
- from Part V - The Appendices
-
- Book:
- From Spinors to Supersymmetry
- Published online:
- 06 July 2023
- Print publication:
- 08 June 2023, pp 947-951
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part IV - Sample Calculations in the Standard Model and Its Supersymmetric Extension
-
- Book:
- From Spinors to Supersymmetry
- Published online:
- 06 July 2023
- Print publication:
- 08 June 2023, pp 665-788
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Part I - Spin-1/2 Fermions in Quantum Field Theory, the Standard Model, and Beyond
-
- Book:
- From Spinors to Supersymmetry
- Published online:
- 06 July 2023
- Print publication:
- 08 June 2023, pp 1-328
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Literature review on maritime cybersecurity: state-of-the-art
-
- Journal:
- The Journal of Navigation / Volume 76 / Issue 4-5 / July 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 06 June 2023, pp. 453-466
- Print publication:
- July 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Necessary condition for the L2 boundedness of the Riesz transform on Heisenberg groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society / Volume 175 / Issue 2 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2023, pp. 445-458
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Sign changes of fourier coefficients of holomorphic cusp forms at norm form arguments
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society / Volume 175 / Issue 3 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 May 2023, pp. 539-567
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the integral Hodge conjecture for varieties with trivial Chow group
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society / Volume 175 / Issue 2 / September 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 May 2023, pp. 433-443
- Print publication:
- September 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Coniveau filtrations and Milnor operation
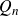 $Q_n$
$Q_n$
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society / Volume 175 / Issue 3 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 May 2023, pp. 521-538
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Zariski dense orbits for regular self-maps of split semiabelian varieties in positive characteristic
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society / Volume 175 / Issue 3 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 May 2023, pp. 479-519
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Positive lower density for prime divisors of generic linear recurrences
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society / Volume 175 / Issue 3 / November 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2023, pp. 467-478
- Print publication:
- November 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation