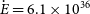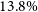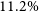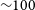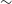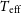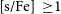Refine search
Actions for selected content:
24896 results in Cosmology, Relativity and Gravitation
Re. I. Understanding galaxy sizes, associated luminosity densities, and the artificial division of the early-type galaxy population – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2024, e015
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Fast as Potoroo: Radio continuum detection of a bow-shock pulsar wind nebula powered by pulsar J1638–4713
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2024, e032
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Galaxy spin direction asymmetry in JWST deep fields
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2024, e038
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Angular momentum and energy transport in disc–jet systems: Unravelling the contribution of saturated thermal conduction
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 March 2024, e023
-
- Article
- Export citation
HINORA, a method for detecting ring-like structures in 3D point distributions I: Application to the Local Volume Galaxy catalogue
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2024, e018
-
- Article
- Export citation
Deblending overlapping galaxies in DECaLS using transformer-based algorithm: A method combining multiple bands and data types
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 March 2024, e035
-
- Article
- Export citation
Predicting the scaling relations between the dark matter halo mass and observables from generalised profiles I: Kinematic tracers
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2024, e020
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
s-Process Enriched Evolved Binaries in the Galaxy and the Magellanic Clouds
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 March 2024, e025
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Calculation of astrophysical reaction rate and uncertainty for T(d,n)4He using Bayesian statistical approach
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 13 March 2024, e019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Are Odd Radio Circles phoenixes of powerful radio galaxies?
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 March 2024, e024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Early accretion onset in long-period isolated pulsars
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, e014
-
- Article
- Export citation
Dark Sage: Next-generation semi-analytic galaxy evolution with multidimensional structure and minimal free parameters
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 27 February 2024, e053
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
EMU/GAMA: A technique for detecting active galactic nuclei in low mass systems
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 21 February 2024, e016
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation

Introduction to Galaxy Formation and Evolution
- From Primordial Gas to Present-Day Galaxies
-
- Published online:
- 09 February 2024
- Print publication:
- 17 October 2019
-
- Textbook
- Export citation
Plane polarisation in Comptonization process: A Monte Carlo study
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, e013
-
- Article
- Export citation
Survey and monitoring of ASKAP’s RFI environment and trends I: Flagging statistics
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, e012
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
A commensal Fast Radio Burst search pipeline for the Murchison Widefield Array
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2024, e011
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
M2P2 I: Maser Monitoring Parkes Program data description and Stokes-I OH maser variability
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 22 January 2024, e009
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Multi-periodicity in the high gravity blue large amplitude pulsator ZTF J071329.02-152125.2
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2024, e010
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
EMU/GAMA: Radio-detected galaxies are more obscured than optically selected galaxies
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 41 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 January 2024, e021
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation