Refine search
Actions for selected content:
106116 results in Materials Science
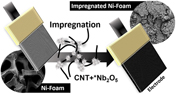
Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis and electrochemical characterization of niobium pentoxide/carbon nanotubes composites
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 January 2019, pp. 592-599
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Biocompatible methionine-capped CdS/ZnS quantum dots for live cell nucleus imaging
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 344-351
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
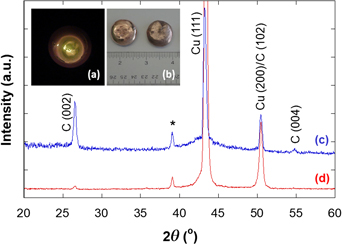
Direct urea fuel cells based on CuNi-plated polymer cloth as a anode catalyst
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 88-91
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Corrosion-resistant nickel thin films by electroless deposition in foam of electrolyte
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 352-359
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Preparation and electrical conductivity of graphitic carbon-infused copper alloys
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 137-143
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Numerical investigation of spherical indentation on elastic-power-law strain-hardening solids with non-equibiaxial residual stresses
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 360-369
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
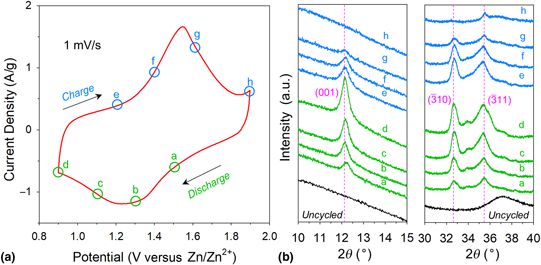
Deciphering charge-storage mechanisms in 3D MnOx@carbon electrode nanoarchitectures for rechargeable zinc-ion cells
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 99-106
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
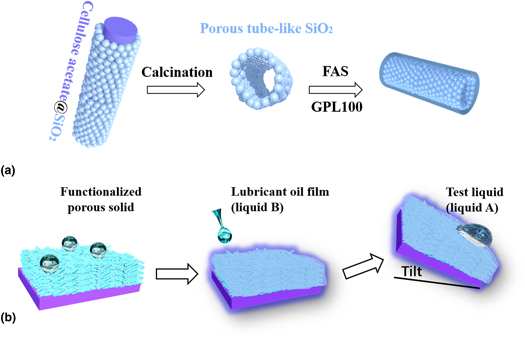
Self-healing liquid-infused surfaces with high transparency for optical devices
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 92-98
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
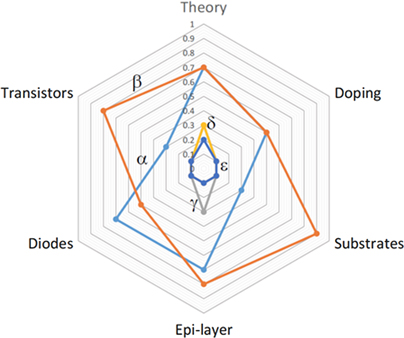
Device processing and junction formation needs for ultra-high power Ga2O3 electronics
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 77-87
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Preparation of nanosized porous oxide layers on titanium by asymmetric AC electrolysis in sulfuric acid
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 194-202
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
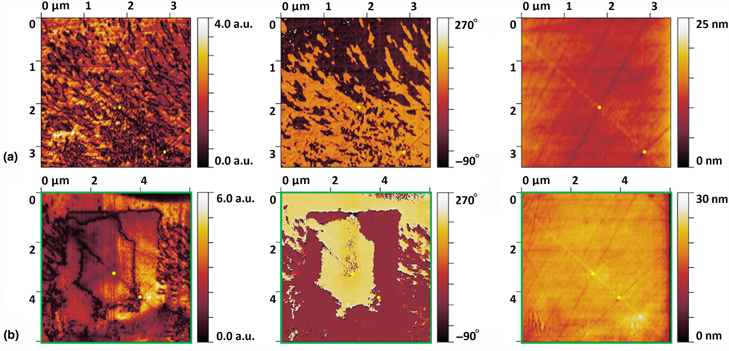
Ferroelectric domain engineering of lithium niobate single crystal confined in glass
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 334-339
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
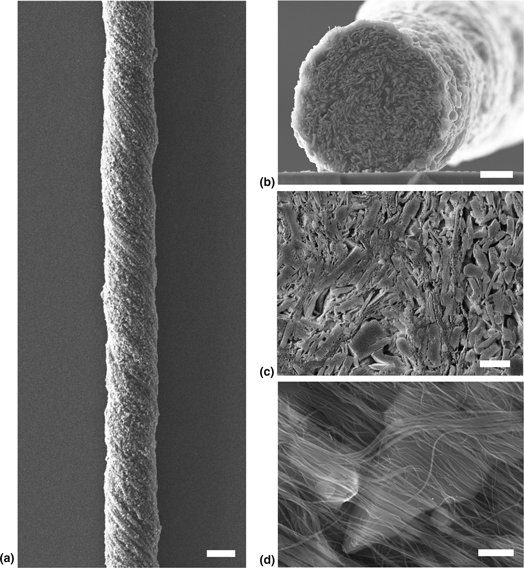
Highly loaded MXene/carbon nanotube yarn electrodes for improved asymmetric supercapacitor performance
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 114-121
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
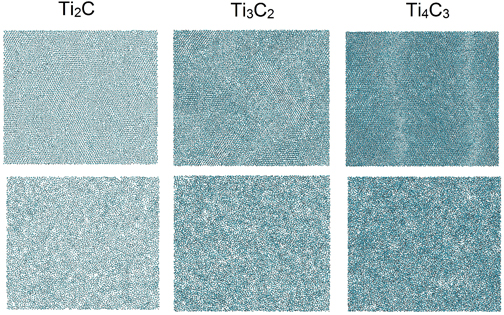
Thermal stability of two-dimensional titanium carbides Tin+1Cn (MXenes) from classical molecular dynamics simulations
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 203-208
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Thermoelectric figure of merit and thermal conductivity of type-I clathrate alloy nanowires
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 370-374
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
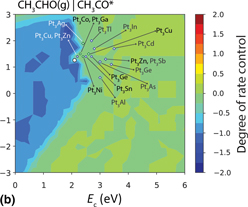
In-silico screening of Pt-based bimetallic alloy catalysts using ab initio microkinetic modeling for non-oxidative dehydrogenation of ethanol to produce acetaldehyde
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 107-113
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
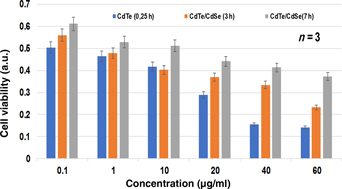
Cell viability study of green synthesized CdTe/CdSe quantum dots against osteosarcoma cell line for improved therapeutic action
-
- Journal:
- MRS Communications / Volume 9 / Issue 1 / March 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. 340-343
- Print publication:
- March 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Synergistic effect of carbon nanotube and graphene nanoplatelet addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ31 prepared using hot-pressing sintering – ERRATUM
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 23 / 16 December 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 January 2019, p. 3975
- Print publication:
- 16 December 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
JMR volume 34 issue 2 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. b1-b5
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
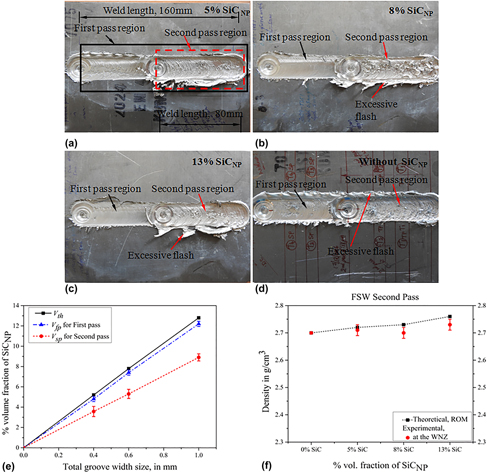
Experimental investigation on effects of varying volume fractions of SiC nanoparticle reinforcement on microstructure and mechanical properties in friction-stir-welded dissimilar joints of AA2024-T351 and AA7075-T651
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 7 / 15 April 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 January 2019, pp. 1229-1247
- Print publication:
- 15 April 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
JMR volume 34 issue 2 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Materials Research / Volume 34 / Issue 2 / 28 January 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 January 2019, pp. f1-f5
- Print publication:
- 28 January 2019
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation