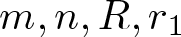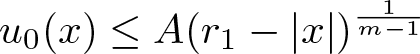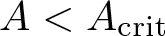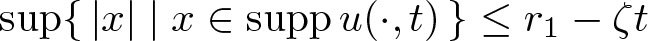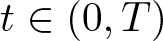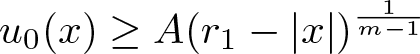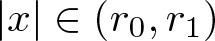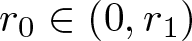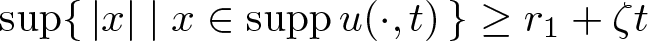Refine listing
Actions for selected content:
1419635 results in Open Access
Kristin Davidse, Ngum Meyuhnsi Njende and Gerard O’Grady, Specificational and presentational there-clefts: Redefining the field of clefts . Cham: Palgrave Macmillan, 2023. Pp. xiii + 187. ISBN 9783031322693.
-
- Journal:
- English Language & Linguistics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2025, pp. 1-7
-
- Article
- Export citation
China’s Belt and Road Initiative and Its Impact on the Energy Independence of the European Union
-
- Journal:
- Asian Journal of Law and Society / Volume 12 / Issue 2 / June 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2025, pp. 274-303
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Medusae morphogenesis by tissue regeneration: a case study on Cassiopea xamachana Bigelow, 1892 (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom / Volume 105 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2025, e112
-
- Article
- Export citation
Shrinking vs. expanding: the evolution of spatial support in degenerate Keller–Segel systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2025, pp. 1-25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Design of a sub-1.4 dB noise figure robust X-band LNA using GaN HEMT technology
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 17 / Issue 6 / July 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2025, pp. 1062-1070
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Double-orifice mitral valve causing left ventricular outflow tract obstruction: a hitherto unreported entity
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 35 / Issue 10 / October 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2025, pp. 2178-2180
-
- Article
- Export citation
Pulmonary valve-in-valve implantation using a Pulsta valve in repaired Tetralogy of Fallot
-
- Journal:
- Cardiology in the Young / Volume 35 / Issue 9 / September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2025, pp. 1962-1964
-
- Article
- Export citation
Behaviour of finite-size floating particles in free-surface turbulence
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1019 / 25 September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2025, A61
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Duality and transform analysis for non-decreasing functionals of stochastic processes and their applications
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2025, pp. 1-27
-
- Article
- Export citation
Tracy L. Steffes. Structuring Inequality: How Schooling, Housing, and Tax Policies Shaped Metropolitan Development and Education Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2024. 376 pp.
-
- Journal:
- History of Education Quarterly / Volume 65 / Issue 4 / November 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2025, pp. 566-569
- Print publication:
- November 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
A Humanist Reconquista: Hernando de Talavera’s Pedagogy of Good Manners and His Residential School for Morisco Boys
-
- Journal:
- History of Education Quarterly / Volume 65 / Issue 4 / November 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 30 September 2025, pp. 498-516
- Print publication:
- November 2025
-
- Article
- Export citation
The New Kingdom of Granada: The Making and Unmaking of Spain’s Atlantic Empire. By Santiago Muñoz-Arbeláez . Durham: Duke University Press, 2025. Pp. 328. $104.95 cloth; $29.95 paper.
-
- Journal:
- The Americas , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2025, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Il Foro Di Sala 2. Gli Scavi Di Jules BorÉly E Khadija Fouad (1929–1930) By Emanuele Papi, Stefano Camporeale, Rossella Pansini (with contributions by Leonardo Bigi, Cesare Felici, Silvio Leone, Luca Passalacqua). Mediterranean Archaeology Studies 5. Edizioni Quasar, Rome, 2022. ISBN 9788854913226, pp. 296, 307 black-and-white and colour figures, 33 tables. Price: €40.00 (paperback), Open Access PDF eBook - Il Foro Di Sala 3. Edifici E Ricostruzioni By Rossella Pansini. Mediterranean Archaeology Studies 6. Edizioni Quasar, Rome, 2023. ISBN 9788854914469, pp. 188, 109 black-and-white and colour figures, 27 tables. Price: €40.00 (paperback), Open Access PDF eBook
-
- Journal:
- Libyan Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2025, pp. 1-3
-
- Article
- Export citation
Mixed-state branching evolution for cell division models
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2025, pp. 1-22
-
- Article
- Export citation
Survival and reproductive performance of Rhopalosiphum padi (Hemiptera: Aphididae) on maize husk: evidence for a secondary host facilitating seasonal carryover
-
- Journal:
- Bulletin of Entomological Research , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2025, pp. 1-11
-
- Article
- Export citation
FLM volume 1019 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Fluid Mechanics / Volume 1019 / 25 September 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2025, p. f1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Elizabeth Shaw, Roman Feet and Shoes: The Cultural Significance of Feet, Footwear, and Their Representations in the North-Western Provinces (BAR International Series S3186.) Oxford: BAR Publishing, 2024. Pp. xvii +176, illus. isbn 9781407361543 (pbk). £55.00.
-
- Journal:
- Britannia , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
- Export citation
Introduction
-
- Journal:
- New Blackfriars ,
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2025, p. 1
-
- Article
- Export citation
Do Politicians Outside the United States Also Think Voters Are More Conservative than They Really Are? – CORRIGENDUM
-
- Journal:
- American Political Science Review , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2025, pp. 1-2
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Intrauterine growth restriction promotes hypothalamic circadian dysregulation in adult mouse offspring
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease / Volume 16 / 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 29 September 2025, e36
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation