Refine search
Actions for selected content:
47865 results in Zoology
An international cross-sectional survey to compare weight and weight gain management in antenatal care across the UK, Ireland, and Australia during the COVID-19 pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE5 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, E304
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Healthier swaps: evaluating the effects of in-store point of sale messaging to encourage choice of ‘healthier’ alternatives to popular products
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE5 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, E326
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Replacement of saturated fatty acids from meats by dairy sources in relation to incident coronary heart diseases in the European Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)-Norfolk study
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE5 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, E349
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Self-perceived food literacy in relation to the quality of overall diet and main meals in Japanese adults: a cross-sectional study
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 82 / Issue OCE5 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2024, E327
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association between sleep duration and quality with food intake, chrononutrition patterns, and weight gain during pregnancy
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 1413-1420
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Associations of childhood diet quality scores with arterial stiffness and carotid artery intima-media thickness in adolescence/early adulthood: findings from the ALSPAC cohort
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 4 / 28 February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 720-735
- Print publication:
- 28 February 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
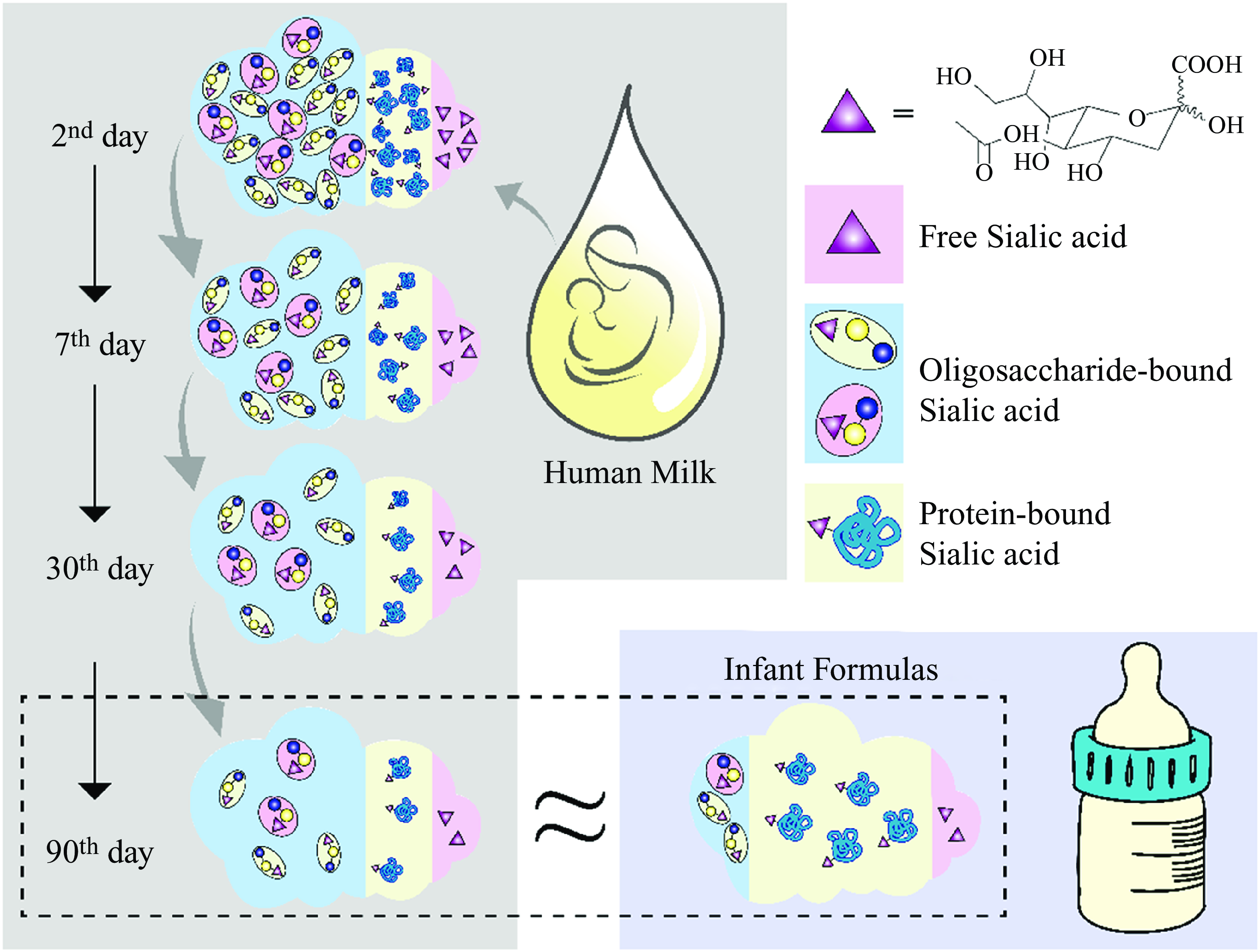
Sialic acid in human milk and infant formulas in China: concentration, distribution and type
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 January 2024, pp. 1506-1512
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Assessing association of household diet diversity with mother’s time use on productive and reproductive activities: a case for gender sensitive social safety nets
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, e33
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Ultra-processed foods consumption among a USA representative sample of middle-older adults: a cross-sectional analysis
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, pp. 1461-1472
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Use of table sugar and non-caloric sweeteners in Brazil: associated factors and changes across a decade
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, pp. 1591-1599
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Trends in ultra-processed food availability and its association with diet-related non-communicable disease health indicators in the Portuguese population
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 9 / 14 May 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, pp. 1600-1607
- Print publication:
- 14 May 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
The environmental impact of beef and ultra-processed food consumption in Brazil
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, e34
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Current evidence on the effectiveness of Ready-to-Use Supplementary Foods in children with moderate acute malnutrition: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Nutritional Science / Volume 12 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 January 2024, e130
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Urban school neighbourhoods dominated by unhealthy food retailers and advertisements in Greater Tunis: a geospatial study in the midst of the nutrition transition
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 January 2024, e44
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Breast-feeding as protective factor against bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2024, pp. 1405-1412
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Comprehensive evaluation of body composition in a wide age range of Iranian adults using bioelectrical impedance analysis: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2024, e24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Effect of fatty acid-enriched black soldier fly larvae meal combined with chitinase on the metabolic processes of Nile tilapia
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2024, pp. 1326-1341
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Implementation and effectiveness of a school-based intervention to increase adherence to national school meal guidelines: a non-randomised controlled trial
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2024, e25
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
PHN volume 26 issue s1 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue S1 / December 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2024, p. b1
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- Export citation
Development and application of a 2-step methodology to select a reference society providing Dietary Reference Values for national implementation
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 02 January 2024, e28
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation