We investigate some aspects of the problem of the estimation of birth distributions (BDs) in multi-type Galton–Watson trees (MGWs) with unobserved types. More precisely, we consider two-type MGWs called spinal-structured trees. This kind of tree is characterized by a spine of special individuals whose BD  $\nu$ is different from the other individuals in the tree (called normal, and whose BD is denoted by
$\nu$ is different from the other individuals in the tree (called normal, and whose BD is denoted by 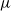 $\mu$). In this work, we show that even in such a very structured two-type population, our ability to distinguish the two types and estimate
$\mu$). In this work, we show that even in such a very structured two-type population, our ability to distinguish the two types and estimate 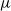 $\mu$ and
$\mu$ and  $\nu$ is constrained by a trade-off between the growth-rate of the population and the similarity of
$\nu$ is constrained by a trade-off between the growth-rate of the population and the similarity of 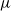 $\mu$ and
$\mu$ and  $\nu$. Indeed, if the growth-rate is too large, large deviation events are likely to be observed in the sampling of the normal individuals, preventing us from distinguishing them from special ones. Roughly speaking, our approach succeeds if
$\nu$. Indeed, if the growth-rate is too large, large deviation events are likely to be observed in the sampling of the normal individuals, preventing us from distinguishing them from special ones. Roughly speaking, our approach succeeds if 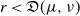 $r\lt \mathfrak{D}(\mu,\nu)$, where r is the exponential growth-rate of the population and
$r\lt \mathfrak{D}(\mu,\nu)$, where r is the exponential growth-rate of the population and 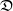 $\mathfrak{D}$ is a divergence measuring the dissimilarity between
$\mathfrak{D}$ is a divergence measuring the dissimilarity between 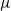 $\mu$ and
$\mu$ and  $\nu$.
$\nu$.