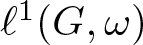Refine search
Actions for selected content:
118 results
Chapter 23 - Body Dissatisfaction Scale for Adults (BDS)
-
-
- Book:
- Handbook of Body Image-Related Measures
- Published online:
- 21 November 2025
- Print publication:
- 20 November 2025, pp 71-72
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 96 - Muscle Silhouette Measure (MSM) and Fat Silhouette Measure (FSM)
-
-
- Book:
- Handbook of Body Image-Related Measures
- Published online:
- 21 November 2025
- Print publication:
- 20 November 2025, pp 288-290
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 28 - Body Esteem Scale for Adolescents and Adults (BESAA)
-
-
- Book:
- Handbook of Body Image-Related Measures
- Published online:
- 21 November 2025
- Print publication:
- 20 November 2025, pp 86-88
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 49 - Body Parts Satisfaction Scale–Revised (BPSS-R)
-
-
- Book:
- Handbook of Body Image-Related Measures
- Published online:
- 21 November 2025
- Print publication:
- 20 November 2025, pp 154-156
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter 47 - Body Matrices
-
-
- Book:
- Handbook of Body Image-Related Measures
- Published online:
- 21 November 2025
- Print publication:
- 20 November 2025, pp 147-150
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Case 15: - Anorexia Nervosa
- from Part 1: - Vignettes
-
- Book:
- Practise Psychiatry
- Published online:
- 04 September 2025
- Print publication:
- 18 September 2025, pp 138-149
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
An extension-restriction theorem for weighted Besov spaces
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Journal of Mathematics , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 26 August 2025, pp. 1-48
-
- Article
- Export citation
8 - Feet
-
- Book:
- Stress and Accent
- Published online:
- 15 March 2025
- Print publication:
- 27 March 2025, pp 257-296
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Intergenerational trends in body size among Moscow’s young adults: socio-demographic influences of the 20th century
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Biosocial Science / Volume 57 / Issue 1 / January 2025
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 January 2025, pp. 57-74
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Growth trajectory at 24 months of preterm infants after discharge: a longitudinal study in Indonesia
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 132 / Issue 10 / 28 November 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 October 2024, pp. 1300-1307
- Print publication:
- 28 November 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Inequalities in diet quality by socio-demographic characteristics, smoking, and weight status in a large UK-based cohort using a new UK diet quality questionnaire-UKDQQ
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Nutritional Science / Volume 13 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 October 2024, e59
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Impact of COVID-19 restriction on weight, physical activity, diet and psychological distress on people with polycystic ovary syndrome
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 83 / Issue OCE1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2024, E82
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Understanding barriers and facilitators to diet and physical activity modification in people with polycystic ovary syndrome: a mixed method systematic review
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Nutrition Society / Volume 83 / Issue OCE1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2024, E81
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Power and the Messiness of Discrimination Law: Reflections on the Role of Power in Sophia Moreau's Faces of Inequality
-
- Journal:
- Dialogue: Canadian Philosophical Review / Revue canadienne de philosophie / Volume 63 / Issue 1 / April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 April 2024, pp. 75-84
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
On the Dales–Żelazko conjecture for Beurling algebras on discrete groups
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 66 / Issue 3 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 July 2023, pp. 613-624
-
- Article
- Export citation
Association of dietary fibre intake with subsequent fasting glucose levels and indicators of adiposity in school-age Japanese children
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 May 2023, pp. 1617-1625
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Association of breakfast skipping with habitual dietary intake and BMI in female rotating shift workers
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 26 / Issue 8 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 April 2023, pp. 1634-1643
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Non-overweight depressed patients who respond to antidepressant treatment have a higher risk of later metabolic syndrome: findings from the METADAP cohort
-
- Journal:
- Psychological Medicine / Volume 53 / Issue 14 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 January 2023, pp. 6560-6569
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Maximum permissible load for Yonaguni ponies (Japanese landrace horses) trotting over a short, straight course
-
- Journal:
- Animal Welfare / Volume 25 / Issue 1 / February 2016
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 151-156
-
- Article
- Export citation
Chapter 23 - Care of the Bariatric Patient
-
-
- Book:
- Fundamentals of Operating Department Practice
- Published online:
- 18 August 2022
- Print publication:
- 08 September 2022, pp 255-263
-
- Chapter
- Export citation