The role of the gut microbiota in coeliac disease (CD) is unclear and evidence remains inconclusive( Reference Stene 1 , Reference Collado 2 ). This study investigated the metabolic activity of the gut microbiota in patients with long standing CD (LS), healthy siblings of CD patients (HS), newly diagnosed CD patients (ND) followed from diagnosis up to one year of gluten free diet (GFD) and healthy controls (HC).
Faecal pH and faecal concentration of ammonia, short chain fatty acids (SCFA), branched chain fatty acids (BCFA), lactate (L and D lactate), and free and total sulphide were measured in spot samples. ND patients provided up to 3 samples (at diagnosis, 6 and 12 month on GFD).
Forty three (23 females, age 9.3 ± 4.3) LS, 23 HS (13 females, age 9 ± 4.6), 11(6 females, 11.4 ± 2.4) ND and 57 HC (30 females, age 8 ± 4.2) participated in the study. The concentrations of propionate (p = 0.024), butyrate (p = 0.004) and valerate (p = 0.011) were significantly lower in the LS group than in HC (Table). Similarly, the concentrations of all BCFA were significantly reduced (iso-butyrate p = 0.016, iso-valeric p = 0.039, iso-caproic p = 0.025) in the LS group compared with HC (Table). There were no statistically significant differences in the concentration of SCFA and BCFA between LS and HS. Total sulphide was significantly increased in the LS group compared to the HC group (p = 0.027).
Table. SCFA and BCFA concentrations in all groups
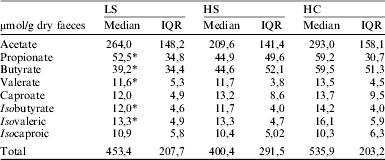
* p < 0.05 compared with HC.
No significant changes were observed in the concentrations of SCFA in ND during GFD. However, compared to disease diagnosis, faecal sulphide significantly increased after 6 (p = 0.014) and 12 months on GFD (p = 0.022).
Major changes were observed in the concentration of faecal bacterial metabolites between children with LS and HC. The reason for these differences is not yet clear but may be explained by the resolution of gastrointestinal malabsorption and the different dietary patterns of those who adhere to a gluten free diet.
This study was funded by the Nutricia Research Foundation.



