Article contents
Estimation of the offspring mean in a supercritical or near-critical size-dependent branching process
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 July 2016
Abstract
We consider a single-type supercritical or near-critical size-dependent branching process {N n }n such that the offspring mean converges to a limit m ≥ 1 with a rate of convergence of order 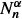 as the population size N n grows to ∞ and the variance may vary at the rate
as the population size N n grows to ∞ and the variance may vary at the rate 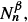 where −1 ≤ β < 1. The offspring mean m(N) = m + μN -α + o(N -α) depends on an unknown parameter θ0 belonging either to the asymptotic model (θ0 = m) or to the transient model (θ0 = μ). We estimate θ0 on the nonextinction set from the observations {N h ,…,N n } by using the conditional least-squares method weighted by
where −1 ≤ β < 1. The offspring mean m(N) = m + μN -α + o(N -α) depends on an unknown parameter θ0 belonging either to the asymptotic model (θ0 = m) or to the transient model (θ0 = μ). We estimate θ0 on the nonextinction set from the observations {N h ,…,N n } by using the conditional least-squares method weighted by 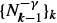 (where γ ∈ ℝ) in the approximate model m θ,ν̂ n (·), where ν̂n is any estimation of the parameter of the nuisance part (O(N -α) if θ0 = m and o(N -α) if θ0 = μ). We study the strong consistency of the estimator of θ0 as γ varies, with either h or n - h remaining constant as n → ∞. We use either a minimum-contrast method or a Taylor approximation of the first derivative of the contrast. The main condition for obtaining strong consistency concerns the asymptotic behavior of the process. We also give the asymptotic distribution of the estimator by using a central-limit theorem for random sums and we show that the best rate of convergence is attained when γ = 1 + β.
(where γ ∈ ℝ) in the approximate model m θ,ν̂ n (·), where ν̂n is any estimation of the parameter of the nuisance part (O(N -α) if θ0 = m and o(N -α) if θ0 = μ). We study the strong consistency of the estimator of θ0 as γ varies, with either h or n - h remaining constant as n → ∞. We use either a minimum-contrast method or a Taylor approximation of the first derivative of the contrast. The main condition for obtaining strong consistency concerns the asymptotic behavior of the process. We also give the asymptotic distribution of the estimator by using a central-limit theorem for random sums and we show that the best rate of convergence is attained when γ = 1 + β.
MSC classification
Information
- Type
- General Applied Probability
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Applied Probability Trust 2004
References
- 11
- Cited by

