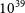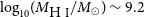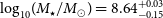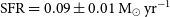Refine search
Actions for selected content:
24897 results in Cosmology, Relativity and Gravitation
CHAPTER IV: CLOSING CEREMONY
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 19 / Issue T31 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2025, pp. 38-43
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
IAU volume 19 issue 374 Cover and Back matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 19 / Issue S374 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 December 2025, pp. b1-b2
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Deep Radio Image Segmentation
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 19 / Issue S368 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2025, pp. 127-128
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Neural Networks for Meteorite and Meteor Recognition
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 19 / Issue S368 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2025, pp. 95-97
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
IAU volume 19 issue T31 Cover and Front matter
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 19 / Issue T31 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2025, pp. f1-f9
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
CHAPTER III: SPECIAL PRESENTATIONS, PLENARY DISCOURSES AND SOCIAL EVENTS
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 19 / Issue T31 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 March 2025, pp. 32-37
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- HTML
- Export citation
Unsupervised clustering visualisation tool for Gaia DR3
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 19 / Issue S368 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2025, pp. 98-100
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Search for Microlensing Signature in Gravitational Waves from Binary Black Hole Events
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union / Volume 19 / Issue S368 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 August 2025, pp. 113-115
- Print publication:
- August 2023
-
- Article
- Export citation
Probing the consistency of cosmological contours for supernova cosmology
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 July 2023, e038
-
- Article
- Export citation
Measuring photometric redshifts for high-redshift radio source surveys
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, e039
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Parkes Pulsar Timing Array third data release
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 July 2023, e049
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The Southern-sky MWA Rapid Two-metre (SMART) pulsar survey—II. Survey status, pulsar census, and first pulsar discoveries – ADDENDUM
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 July 2023, e031
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
The host galaxy of FRB 20171020A revisited
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 July 2023, e029
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Survey-scale discovery-based research processes: Evaluating a bespoke visualisation environment for astronomical survey data
-
- Journal:
- Publications of the Astronomical Society of Australia / Volume 40 / 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2023, e035
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
7 - Cosmology and the Big Bang
-
- Book:
- Einstein's General Theory of Relativity
- Published online:
- 15 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp 139-176
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Frontmatter
-
- Book:
- Einstein's General Theory of Relativity
- Published online:
- 15 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp i-iv
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
3 - Geodesics
-
- Book:
- Einstein's General Theory of Relativity
- Published online:
- 15 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp 44-84
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Dedication
-
- Book:
- Einstein's General Theory of Relativity
- Published online:
- 15 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp v-vi
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Appendix B - The Riemann Tensor
-
- Book:
- Einstein's General Theory of Relativity
- Published online:
- 15 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp 178-186
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Appendix E - Robertson-Walker Space-Time
-
- Book:
- Einstein's General Theory of Relativity
- Published online:
- 15 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 29 June 2023, pp 195-197
-
- Chapter
- Export citation