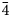212 results
11 - Social Democracy and the Cold War
- from IV - 1931–76: Society Triumphant
-
- Book:
- Modern Britain, 1750 to the Present
- Published online:
- 14 January 2025
- Print publication:
- 30 January 2025, pp 396-434
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Chapter One - Imperialism and the Origins of Constitutions
-
- Book:
- A Sociology of Post-Imperial Constitutions
- Published online:
- 06 December 2024
- Print publication:
- 12 December 2024, pp 38-107
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Psychological Type and Temperament Profile of Anglican Clergy Serving in the Episcopal Church (USA)
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Anglican Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2024, pp. 1-14
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
8 - The International Criminal Court
- from Part III - International Prosecution
-
- Book:
- An Introduction to International Criminal Law and Procedure
- Published online:
- 07 November 2024
- Print publication:
- 18 July 2024, pp 134-162
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Associations between food insecurity and diabetes risk factors in US adolescents in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2007–2016
-
- Journal:
- Public Health Nutrition / Volume 27 / Issue 1 / 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 12 February 2024, e68
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
6 - Right-Wing Populism in the USA
-
- Book:
- Democracy's Resilience to Populism's Threat
- Published online:
- 11 January 2024
- Print publication:
- 25 January 2024, pp 196-226
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Ultra-processed foods consumption among a USA representative sample of middle-older adults: a cross-sectional analysis
-
- Journal:
- British Journal of Nutrition / Volume 131 / Issue 8 / 28 April 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 January 2024, pp. 1461-1472
- Print publication:
- 28 April 2024
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Clay Mineral Changes in the Morrow Experimental Plots, University of Illinois
-
- Journal:
- Clays and Clay Minerals / Volume 50 / Issue 3 / June 2002
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2024, pp. 364-370
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Predictors of Perceived Changes in Psychological Wellbeing among Clergy in the USA Serving in the Episcopal Church during the 2021 Covid-19 Pandemic
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Anglican Studies , First View
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 18 October 2023, pp. 1-24
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Tellurium-rich stibiogoldfieldite and Se-bearing dantopaite from Goldfield, Nevada, USA: new crystal chemical data
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 88 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 16 October 2023, pp. 40-48
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Chapter 8 - Puccini the Long-Distance Traveller
- from Part II - Puccini’s Places
-
-
- Book:
- Puccini in Context
- Published online:
- 31 August 2023
- Print publication:
- 14 September 2023, pp 61-70
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
The trace-element compositions of amphibole, magnetite and ilmenite as potential exploration guides to metamorphosed Proterozoic Cu–Zn±Pb±Au±Ag volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits in Colorado, USA
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 88 / Issue 1 / February 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 11 September 2023, pp. 61-89
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
6 - Comparing Cultures
-
- Book:
- Language, Discourse and Anxiety
- Published online:
- 08 June 2023
- Print publication:
- 22 June 2023, pp 166-190
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Introduction
-
- Book:
- Holding Out
- Published online:
- 31 March 2023
- Print publication:
- 20 April 2023, pp 1-33
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Libbyite, (NH4)2(Na2□)[(UO2)2(SO4)3(H2O)]2⋅7H2O, a new mineral with uranyl–sulfate sheets from the Blue Lizard mine, San Juan County, Utah, USA
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 87 / Issue 5 / October 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 19 April 2023, pp. 767-772
-
- Article
- Export citation
5 - The Objectives of Regulating the Data-Driven Economy
-
- Book:
- Regulating Access and Transfer of Data
- Published online:
- 06 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 13 April 2023, pp 151-166
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
16 - International Action: Personal Views
-
- Book:
- Why Mothers Died and How their Lives are Saved
- Published online:
- 05 April 2023
- Print publication:
- 30 March 2023, pp 207-226
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
5 - Frozen Parties, Failing Markets
-
- Book:
- The Age of Discontent
- Published online:
- 02 March 2023
- Print publication:
- 09 March 2023, pp 95-128
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Zincorietveldite, Zn(UO2)(SO4)2(H2O)5, the zinc analogue of rietveldite from the Blue Lizard mine, San Juan County, Utah, USA
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 87 / Issue 4 / August 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 03 March 2023, pp. 528-533
-
- Article
- Export citation