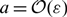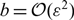Refine search
Actions for selected content:
2 results
Spikes and localised patterns for a novel Schnakenberg model in the semi-strong interaction regime
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- European Journal of Applied Mathematics / Volume 33 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 25 January 2021, pp. 133-152
-
- Article
- Export citation
Isolas of multi-pulse solutions to lattice dynamical systems
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. Section A: Mathematics / Volume 151 / Issue 3 / June 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 July 2020, pp. 916-952
- Print publication:
- June 2021
-
- Article
- Export citation