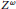Refine search
Actions for selected content:
2 results
Infinite Powers and Cohen Reals
-
- Journal:
- Canadian Mathematical Bulletin / Volume 61 / Issue 4 / 01 December 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 20 November 2018, pp. 812-821
- Print publication:
- 01 December 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation
Initial validation of a transdiagnostic compulsivity questionnaire: the Cambridge–Chicago Compulsivity Trait Scale
-
- Journal:
- CNS Spectrums / Volume 23 / Issue 5 / October 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 May 2018, pp. 340-346
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation