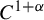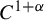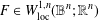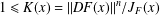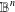Refine search
Actions for selected content:
28 results
4 - The Comparative Advantage-defying, Catching-up Strategy and China’s Traditional Economic System
-
- Book:
- Demystifying the Chinese Economy
- Published online:
- 12 December 2025
- Print publication:
- 08 January 2026, pp 72-100
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
4 - Bipolar Junction Transistors
-
- Book:
- Basic Electronics for Scientists and Engineers
- Published online:
- 23 December 2025
- Print publication:
- 20 November 2025, pp 119-151
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
23 - Distorting the Press
- from Part VI - Supporting the Press Function
-
-
- Book:
- The Future of Press Freedom
- Published online:
- 25 July 2025
- Print publication:
- 24 July 2025, pp 391-414
-
- Chapter
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
7 - Stompbox Revolution: Electric Guitar Pedals and Tone
- from Part II - Technology and Timbre
-
-
- Book:
- The Cambridge Companion to the Electric Guitar
- Published online:
- 08 November 2024
- Print publication:
- 17 October 2024, pp 111-128
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
10 - Franz Schubert, Death and the Gothic
- from Part III - Sound and Musical Imagery
-
-
- Book:
- Schubert's Piano
- Published online:
- 31 August 2024
- Print publication:
- 17 October 2024, pp 201-218
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Effects of distortion on a BLI fan
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 128 / Issue 1325 / July 2024
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 09 May 2024, pp. 1362-1378
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
20 - Electronics and Music
-
- Book:
- Physics Behind Music
- Published online:
- 24 May 2023
- Print publication:
- 06 April 2023, pp 376-389
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Predecisional information distortion in physicians’ diagnostic judgments: Strengthening a leading hypothesis or weakening its competitor?
-
- Journal:
- Judgment and Decision Making / Volume 9 / Issue 6 / November 2014
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 01 January 2023, pp. 572-585
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Design of a sub-scale fan for a boundary layer ingestion test with by-pass flow
-
- Journal:
- The Aeronautical Journal / Volume 126 / Issue 1302 / August 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 17 August 2022, pp. 1288-1302
-
- Article
- Export citation
Distortion in the group of circle homeomorphisms
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 43 / Issue 4 / April 2023
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 23 March 2022, pp. 1081-1086
- Print publication:
- April 2023
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Further properties of fractional stochastic dominance
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of Applied Probability / Volume 59 / Issue 1 / March 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 28 March 2022, pp. 202-223
- Print publication:
- March 2022
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
Epilogue - Afterlives (1955–Present)
-
- Book:
- Black Legend
- Published online:
- 06 January 2022
- Print publication:
- 06 January 2022, pp 340-357
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
3 - Structure Theory
-
- Book:
- Coarse Geometry of Topological Groups
- Published online:
- 16 December 2021
- Print publication:
- 16 December 2021, pp 68-124
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
Examples of distorted interval diffeomorphisms of intermediate regularity
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Ergodic Theory and Dynamical Systems / Volume 42 / Issue 11 / November 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 08 September 2021, pp. 3311-3324
- Print publication:
- November 2022
-
- Article
- Export citation
Signal distortions in circular dielectric waveguides at mm-wave frequencies
-
- Journal:
- International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies / Volume 14 / Issue 1 / February 2022
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 10 March 2021, pp. 8-18
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Open access
- HTML
- Export citation
1 - Policy, Regulation, and Innovation in China’s Electricity and Telecom Industries
-
-
- Book:
- Policy, Regulation and Innovation in China's Electricity and Telecom Industries
- Published online:
- 08 June 2019
- Print publication:
- 30 May 2019, pp 1-51
-
- Chapter
- Export citation
CAT BOND PRICING UNDER A PRODUCT PROBABILITY MEASURE WITH POT RISK CHARACTERIZATION
-
- Journal:
- ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA / Volume 49 / Issue 2 / May 2019
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 24 April 2019, pp. 457-490
- Print publication:
- May 2019
-
- Article
- Export citation
Crystal structure of a synthetic aluminoan tantalian titanite: a reconnaissance study
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 70 / Issue 1 / February 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 115-121
-
- Article
- Export citation
57Fe Mössbauer effect study of bannisterite: a modulated 2:1-type phyllosilicate
-
- Journal:
- Mineralogical Magazine / Volume 70 / Issue 2 / April 2006
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 05 July 2018, pp. 187-199
-
- Article
- Export citation
UNIQUENESS THEOREMS FOR MAPPINGS OF FINITE DISTORTION
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Journal of the Australian Mathematical Society / Volume 104 / Issue 3 / June 2018
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 07 November 2017, pp. 412-429
- Print publication:
- June 2018
-
- Article
-
- You have access
- Export citation