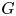Refine search
Actions for selected content:
1 results
Brauer indecomposability of Scott modules with semidihedral vertex
- Part of
-
- Journal:
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society / Volume 64 / Issue 2 / May 2021
- Published online by Cambridge University Press:
- 04 May 2021, pp. 174-182
-
- Article
- Export citation