No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 21 March 2022
Given any rectangular polyhedron 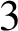 $3$
-manifold
$3$
-manifold 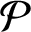 $\mathcal {P}$
tiled with unit cubes, we find infinitely many explicit directions related to cubic algebraic numbers such that all half-infinite geodesics in these directions are uniformly distributed in
$\mathcal {P}$
tiled with unit cubes, we find infinitely many explicit directions related to cubic algebraic numbers such that all half-infinite geodesics in these directions are uniformly distributed in 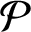 $\mathcal {P}$
.
$\mathcal {P}$
.
Communicated by Dzmitry Badziahin
Please note a has been issued for this article.