In Fig. 1 of Jamwal et al. (Reference Jamwal, Takpa and Parsons2018) the international borders were depicted incorrectly in the inset map. The correct figure is provided here. The international boundaries in this figure were taken from the 1:10 million breakaway and disputed areas shapefile provided by NaturalEarth (Reference Jamwal, Takpa and Parsons2018).
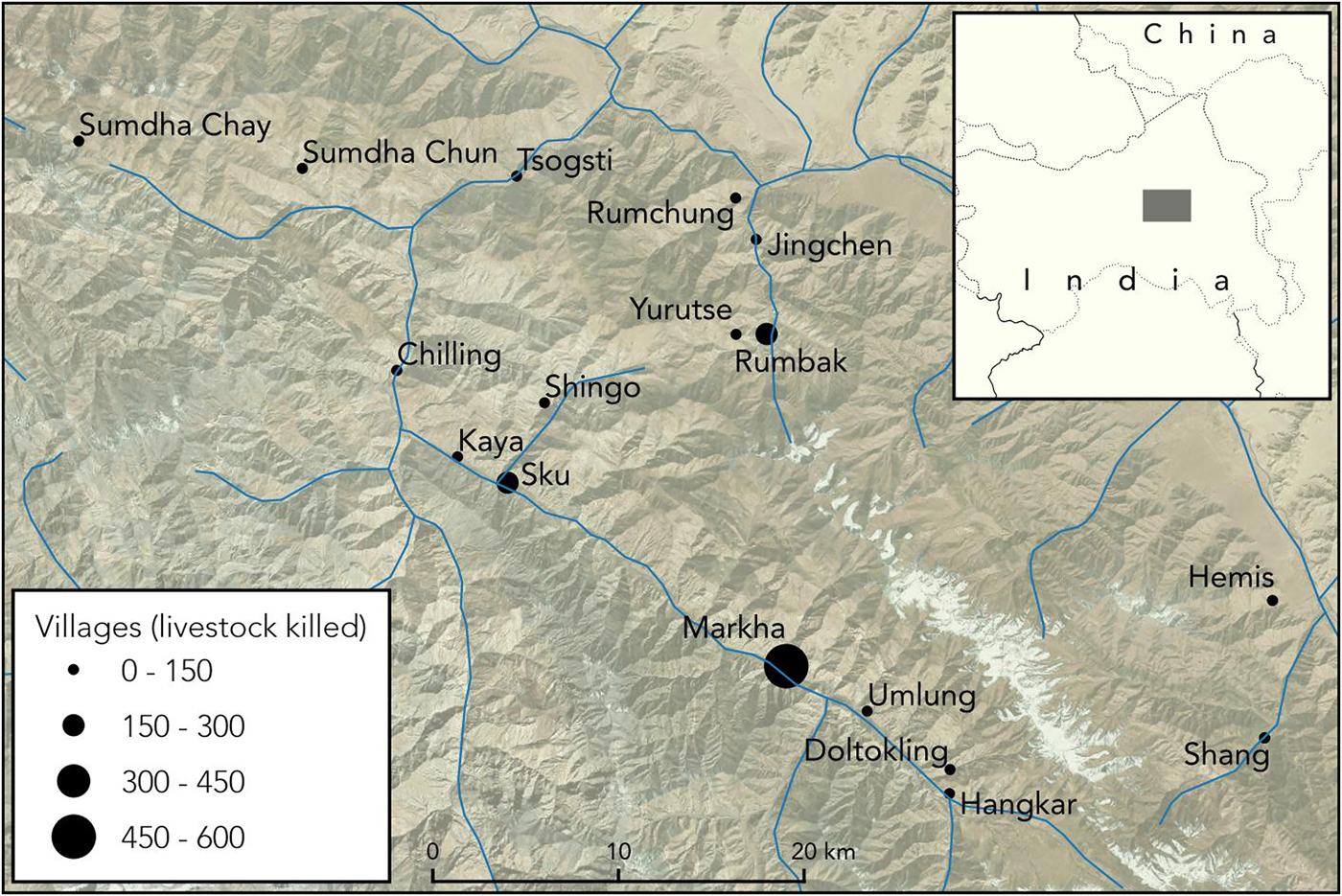
Fig. 1 Hemis National Park and associated villages, with the total number of depredation events by snow leopards Panthera uncia, as reported per village during 1992–2013 (circle size is proportional to the number of events).


