Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Lagrée, P.-Y.
and
Ivan-Fernolendt, A.
2004.
Direct comparison of simplified models of surface reacting flows in flow chambers.
The European Physical Journal Applied Physics,
Vol. 26,
Issue. 2,
p.
133.
Lagrée, Pierre-Yves
and
Lorthois, Sylvie
2005.
The RNS/Prandtl equations and their link with other asymptotic descriptions: Application to the wall shear stress scaling in a constricted pipe.
International Journal of Engineering Science,
Vol. 43,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
352.
Mazeyrat, Johan
Romain, Olivier
Garda, Patrick
Flecher, Erwan
Karouia, Mourad
Leprince, Pascal
Lagree, Pierre-Yves
and
Destrade, Michel
2006.
Wireless communicative stent for follow-up of abdominal aortic aneurysm.
p.
237.
Fullana, J.-M.
Dispot, N.
Flaud, P.
and
Rossi, M.
2007.
An inverse method for non-invasive viscosity measurements.
The European Physical Journal Applied Physics,
Vol. 38,
Issue. 1,
p.
79.
Maerefat, Mehdi
Rahgozar, Saeed
and
Mokhtari-D, Manijhe
2007.
Estimation of Elasticity by Modeling Blood Flow Using Clinical Ultrasound Data.
Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences,
Vol. 10,
Issue. 15,
p.
2569.
Mazeyrat, Johan
Romain, Olivier
Garda, Patrick
Lagree, Pierre-Yves
Destrade, Michel
Karouia, Mourad
and
Leprince, Pascal
2007.
ENDOCOM : Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm test bench for in vitro simulation.
p.
2323.
Avril, Stephane
Huntley, Jonathan M.
and
Cusack, Rhodri
2009.
In vivo measurements of blood viscosity and wall stiffness in the carotid using PC-MRI.
European Journal of Computational Mechanics,
Vol. 18,
Issue. 1,
p.
9.
Saito, Masashi
Ikenaga, Yuki
Matsukawa, Mami
Watanabe, Yoshiaki
Asada, Takaaki
and
Lagree, Pierre-Yves
2011.
1D model for propagation of pulse wave in an arterial network: Comparative study of theory and experiment.
p.
713.
Perego, Mauro
Veneziani, Alessandro
and
Vergara, Christian
2011.
A Variational Approach for Estimating the Compliance of the Cardiovascular Tissue: An Inverse Fluid-Structure Interaction Problem.
SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing,
Vol. 33,
Issue. 3,
p.
1181.
Saito, Masashi
Ikenaga, Yuki
Matsukawa, Mami
Watanabe, Yoshiaki
Asada, Takaaki
and
Lagrée, Pierre-Yves
2011.
One-Dimensional Model for Propagation of a Pressure Wave in a Model of the Human Arterial Network: Comparison of Theoretical and Experimental Results.
Journal of Biomechanical Engineering,
Vol. 133,
Issue. 12,
Degroote, Joris
Couckuyt, Ivo
Vierendeels, Jan
Segers, Patrick
and
Dhaene, Tom
2012.
Inverse modelling of an aneurysm’s stiffness using surrogate-based optimization and fluid-structure interaction simulations.
Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization,
Vol. 46,
Issue. 3,
p.
457.
Bertoglio, Cristóbal
Moireau, Philippe
and
Gerbeau, Jean‐Frederic
2012.
Sequential parameter estimation for fluid–structure problems: Application to hemodynamics.
International Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering,
Vol. 28,
Issue. 4,
p.
434.
Bertoglio, C.
Chapelle, D.
Fernández, M.A.
Gerbeau, J.-F.
and
Moireau, P.
2013.
State observers of a vascular fluid–structure interaction model through measurements in the solid.
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,
Vol. 256,
Issue. ,
p.
149.
Degroote, Joris
Hojjat, Majid
Stavropoulou, Electra
Wüchner, Roland
and
Bletzinger, Kai-Uwe
2013.
Partitioned solution of an unsteady adjoint for strongly coupled fluid-structure interactions and application to parameter identification of a one-dimensional problem.
Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization,
Vol. 47,
Issue. 1,
p.
77.
Bertoglio, Cristóbal
Barber, David
Gaddum, Nicholas
Valverde, Israel
Rutten, Marcel
Beerbaum, Philipp
Moireau, Philippe
Hose, Rodney
and
Gerbeau, Jean-Frédéric
2014.
Identification of artery wall stiffness: In vitro validation and in vivo results of a data assimilation procedure applied to a 3D fluid–structure interaction model.
Journal of Biomechanics,
Vol. 47,
Issue. 5,
p.
1027.
Coullon, Hélène
Fullana, Jose-Maria
Lagrée, Pierre-Yves
Limet, Sébastien
and
Wang, Xiaofei
2014.
Blood Flow Arterial Network Simulation with the Implicit Parallelism Library SkelGIS.
Procedia Computer Science,
Vol. 29,
Issue. ,
p.
102.
Wang, Xiaofei
Fullana, Jose-Maria
and
Lagrée, Pierre-Yves
2015.
Verification and comparison of four numerical schemes for a 1D viscoelastic blood flow model.
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering,
Vol. 18,
Issue. 15,
p.
1704.
Wang, Xiao-Fei
Nishi, Shohei
Matsukawa, Mami
Ghigo, Arthur
Lagrée, Pierre-Yves
and
Fullana, Jose-Maria
2016.
Fluid friction and wall viscosity of the 1D blood flow model.
Journal of Biomechanics,
Vol. 49,
Issue. 4,
p.
565.
Ghigo, A.R.
Delestre, O.
Fullana, J.-M.
and
Lagrée, P.-Y.
2017.
Low-Shapiro hydrostatic reconstruction technique for blood flow simulation in large arteries with varying geometrical and mechanical properties.
Journal of Computational Physics,
Vol. 331,
Issue. ,
p.
108.
Ghigo, Arthur R.
Fullana, Jose-Maria
and
Lagrée, Pierre-Yves
2017.
A 2D nonlinear multiring model for blood flow in large elastic arteries.
Journal of Computational Physics,
Vol. 350,
Issue. ,
p.
136.
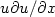 term). Then, using a methodanalogous to the well known Von Kármán-Pohlhausen method fromaeronautics but transposed here for a pulsatile flow, we build a system ofthree coupled non-linear partial differential equations depending only ontime and axial co-ordinate. This system governs the dynamics of internalartery radius, centre velocity and a quantity related to the presence ofviscous effects. These two methods give nearly the same numerical results.Second, we construct an inverse method: the aim is to findfor the simpleintegral model, the physical parameters to put in the "boundary layer" code(simulating clinical data). This is done by varying in the integralmodel the viscosity and elasticity in order to fit best with the data. Toachieve this in a rational way, we have to minimise a cost function, whichinvolves the computation of the adjoint system of the integral method. The good setof parameters (i.e. viscosity, and two coefficients of a wall law)is effectively found again. It opens the perspective for application in realclinical cases of this new non-invasive method for evaluating the viscosityof the flow and elasticity of the wall.
term). Then, using a methodanalogous to the well known Von Kármán-Pohlhausen method fromaeronautics but transposed here for a pulsatile flow, we build a system ofthree coupled non-linear partial differential equations depending only ontime and axial co-ordinate. This system governs the dynamics of internalartery radius, centre velocity and a quantity related to the presence ofviscous effects. These two methods give nearly the same numerical results.Second, we construct an inverse method: the aim is to findfor the simpleintegral model, the physical parameters to put in the "boundary layer" code(simulating clinical data). This is done by varying in the integralmodel the viscosity and elasticity in order to fit best with the data. Toachieve this in a rational way, we have to minimise a cost function, whichinvolves the computation of the adjoint system of the integral method. The good setof parameters (i.e. viscosity, and two coefficients of a wall law)is effectively found again. It opens the perspective for application in realclinical cases of this new non-invasive method for evaluating the viscosityof the flow and elasticity of the wall.
