Published online by Cambridge University Press: 17 August 2023
We study the correlation between the non-thermal velocity dispersion (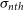 $\sigma_{nth}$) and the length scale (L) in the neutral interstellar medium (ISM) using a large number of Hi gas components taken from various published Hi surveys and previous Hi studies. We notice that above the length-scale (L) of 0.40 pc, there is a power-law relationship between
$\sigma_{nth}$) and the length scale (L) in the neutral interstellar medium (ISM) using a large number of Hi gas components taken from various published Hi surveys and previous Hi studies. We notice that above the length-scale (L) of 0.40 pc, there is a power-law relationship between 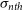 $\sigma_{nth}$ and L. However, below 0.40 pc, there is a break in the power law, where
$\sigma_{nth}$ and L. However, below 0.40 pc, there is a break in the power law, where 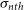 $\sigma_{nth}$ is not significantly correlated with L. It has been observed from the Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method that for the dataset of L
$\sigma_{nth}$ is not significantly correlated with L. It has been observed from the Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method that for the dataset of L 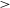 $\gt$ 0.40 pc, the most probable values of intensity (A) and power-law index (p) are 1.14 and 0.55, respectively. Result of p suggests that the power law is steeper than the standard Kolmogorov law of turbulence. This is due to the dominance of clouds in the cold neutral medium. This is even more clear when we separate the clouds into two categories: one for L is
$\gt$ 0.40 pc, the most probable values of intensity (A) and power-law index (p) are 1.14 and 0.55, respectively. Result of p suggests that the power law is steeper than the standard Kolmogorov law of turbulence. This is due to the dominance of clouds in the cold neutral medium. This is even more clear when we separate the clouds into two categories: one for L is 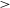 $\gt$ 0.40 pc and the kinetic temperature (
$\gt$ 0.40 pc and the kinetic temperature (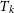 $T_{k}$) is
$T_{k}$) is  $\lt$250 K, which are in the cold neutral medium (CNM) and for other one where L is
$\lt$250 K, which are in the cold neutral medium (CNM) and for other one where L is 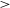 $\gt$0.40 pc and
$\gt$0.40 pc and 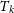 $T_{k}$ is between 250 and 5 000 K, which are in the thermally unstable phase (UNM). Most probable values of A and p are 1.14 and 0.67, respectively, in the CNM phase and 1.01 and 0.52, respectively, in the UNM phase. A greater number of data points is effective for the UNM phase in constructing a more accurate estimate of A and p, since most of the clouds in the UNM phase lie below 500 K. However, from the value of p in the CNM phase, it appears that there is a significant difference from the Kolmogorov scaling, which can be attributed to a shock-dominated medium.
$T_{k}$ is between 250 and 5 000 K, which are in the thermally unstable phase (UNM). Most probable values of A and p are 1.14 and 0.67, respectively, in the CNM phase and 1.01 and 0.52, respectively, in the UNM phase. A greater number of data points is effective for the UNM phase in constructing a more accurate estimate of A and p, since most of the clouds in the UNM phase lie below 500 K. However, from the value of p in the CNM phase, it appears that there is a significant difference from the Kolmogorov scaling, which can be attributed to a shock-dominated medium.
To send this article to your Kindle, first ensure no-reply@cambridge.org is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about sending to your Kindle. Find out more about saving to your Kindle.
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service.
To save this article to your Dropbox account, please select one or more formats and confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you used this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your Dropbox account. Find out more about saving content to Dropbox.
To save this article to your Google Drive account, please select one or more formats and confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you used this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your Google Drive account. Find out more about saving content to Google Drive.