No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Observational Study of Reynolds Stresses Associated with Solar Inertial Modes
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 23 December 2024
Abstract
We study the m = 1 high-latitude inertial mode and its contribution to the latitudinal transport of the Sun’s angular momentum. Ring-diagram helioseismology applied to 5° tiles is used to obtain the horizontal flows near the surface of the Sun. Using 10 years of data from SDO/HMI, we report on the horizontal eigenfunction and Reynolds stress 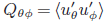 $\[{Q_{\theta \phi }} = \langle {u'_\theta }{u'_\phi }\rangle \]$ for the m = 1 high-latitude inertial mode (frequency –86.3 nHz, critical latitudes ±58°). We find that Qθφ takes significant values above the critical latitude and is positive (negative) in the northern (southern) hemisphere, implying equatorward transport of angular momentum. The Qθφ peaks above latitude 70° with a value of 38 m2/s2.
$\[{Q_{\theta \phi }} = \langle {u'_\theta }{u'_\phi }\rangle \]$ for the m = 1 high-latitude inertial mode (frequency –86.3 nHz, critical latitudes ±58°). We find that Qθφ takes significant values above the critical latitude and is positive (negative) in the northern (southern) hemisphere, implying equatorward transport of angular momentum. The Qθφ peaks above latitude 70° with a value of 38 m2/s2.
Information
- Type
- Contributed Paper
- Information
- Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union , Volume 19 , Symposium S365: Dynamics of Solar and Stellar Convection Zones and Atmospheres , December 2023 , pp. 235 - 239
- Copyright
- © The Author(s), 2024. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of International Astronomical Union


