Article contents
Microrheology study of semidiluted deoxyribonucleic acid solutions
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 01 February 2011
Abstract
Linear rheological behavior and Microrheology measurements of sodium salt calf-thymus DNA aqueous solutions as a function of concentration are reported here. The microrheological behavior was obtained by a combination of experimental techniques: mechanical Rheometry and Dynamic light scattering (DLS). The viscoelastic properties of DNA in water as a function of concentration were performed at 20 °C and rheological and microrhelogical curves were performed. The result indicated that for concentrations lower than the entanglement concentration (Ce ) the system exhibits a predominantly viscous behavior, whereas for higher concentrations exhibits a predominantly elastic behavior. The plateau modulus (G0 ) and the zero complex viscosity () follow a power law concentration dependence of the form: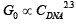 and
and 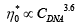 , respectively The microrheology results overlap perfectly in a single line with the mechanical rheology results, extending the time resolution to faster breathing modes
, respectively The microrheology results overlap perfectly in a single line with the mechanical rheology results, extending the time resolution to faster breathing modes
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2010
References
- 1
- Cited by

