Article contents
Diffusion of Gold into Heavily Boron-Doped Silicon
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 February 2011
Abstract
Diffusion of Au into dislocation-free and highly dislocated Si with high B-background doping levels has been investigated with the aid of neutron activation analysis in conjunction with mechanical sectioning. The high B-doping level causes extrinsic conditions, i.e., the hole concentration exceeds the intrinsic carrier concentration even at diffusion temperatures between 900°C and 1100°C. All profiles are accurately described on the basis of the kick-out diffusion model and a mechanism which takes into account segregation of Au at dislocations. Our analysis provides solubility data 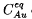 of Au in Si and effective diffusion coefficients
of Au in Si and effective diffusion coefficients 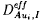 related to interstitial Au and Si self-interstitials I. The dependence of these quantities on the B-background doping level is well described by the Fermi-level effect. This analysis supports singly positively charged states in p-type Si of Au on interstitial (Au i ) and substitutional (Au s ) sites and of Si self-interstitials. Successful fitting of
related to interstitial Au and Si self-interstitials I. The dependence of these quantities on the B-background doping level is well described by the Fermi-level effect. This analysis supports singly positively charged states in p-type Si of Au on interstitial (Au i ) and substitutional (Au s ) sites and of Si self-interstitials. Successful fitting of 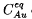 additionally requires an acceptor level of Au s . The electrical properties deduced for Au i , Au s and I are summarized in Table 2. Au profiles in highly dislocated Si obtained especially after diffusion at 900° C give evidence of Au trapped at dislocations. From our preliminary experimental results we determine an enthalpy difference of 2.7 eV between Au on substitutional sites and Au captured at dislocations.
additionally requires an acceptor level of Au s . The electrical properties deduced for Au i , Au s and I are summarized in Table 2. Au profiles in highly dislocated Si obtained especially after diffusion at 900° C give evidence of Au trapped at dislocations. From our preliminary experimental results we determine an enthalpy difference of 2.7 eV between Au on substitutional sites and Au captured at dislocations.
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 1997
References
REFERENCES
- 6
- Cited by

