Article contents
Transmission surface plasmon resonance image detection by a smartphone camera
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 26 July 2018
Abstract
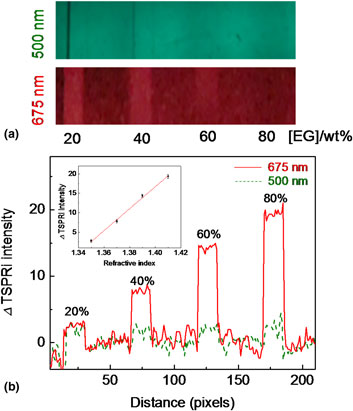
A transmission surface plasmon resonance image (TSPRi) obtained with a plasmonic grating structure was investigated in combination with a smartphone camera. A substrate of a gold-coated CYTOP grating/glass slide showed the TSPR excitation wavelength of 675 nm at the incident light angle of 30°. The TSPRi acquired from a smartphone camera assembled with liquid crystal tunable filters corresponded with spectroscopic results. The sensitivity of this technique was 282/RIU. Due to changes in the sensitivity of the TSPRi intensity to the refractive index of the environment, this technique can be further developed for portable devices for sensor applications.
Information
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2018
References
1.Ebbesen, T.W., Lezec, H.J., Ghaemi, H.F., Thio, T., and Wolff, P.A.: Extraordinary optical transmission through sub-wavelength hole arrays. Nature 391, 667 (1998).Google Scholar
2.Lertvachirapaiboon, C., Baba, A., Ekgasit, S., Shinbo, K., Kato, K., and Kaneko, F.: Transmission surface plasmon resonance techniques and their potential biosensor applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 99, 399 (2018).Google Scholar
3.Singh, B.K. and Hiller, A.C.: Surface plasmon resonance imaging of biomolecular interactions on a grating-based sensor array. Anal. Chem. 78, 2009 (2006).Google Scholar
4.Singh, B.K. and Hiller, A.C.: Surface plasmon resonance enhanced transmission of light gold-coated diffraction gratings. Anal. Chem. 80, 3803 (2008).Google Scholar
5.Yeh, W.H., Kleingartner, J., and Hillier, A.C.: Wavelength tunable surface plasmon resonance-enhanced optical transmission through a chirped diffraction grating. Anal. Chem. 82, 4988 (2010).Google Scholar
6.Yeh, W.H., Petefish, J.W., and Hillier, A.C.: Diffraction-based tracking of surface plasmon resonance enhanced transmission through a gold-coated grating. Anal. Chem. 83, 6047 (2011).Google Scholar
7.Yeh, W.H. and Hillier, A.C.: Use of dispersion imaging for grating-coupled surface plasmon resonance sensing of multilayer Langmuir-Blodgett films. Anal. Chem. 85, 4080 (2013).Google Scholar
8.Turker, B., Guner, H., Ayas, S., Ekiz, O.O., Acar, H., Guler, M.O., and Dâna, A.: Grating coupler integrated photodiodes for plasmon resonance based sensing. Lab. Chip 11, 282 (2010).Google Scholar
9.Baba, A., Tada, K., Janmanee, R., Sriwichai, S., Shinbo, K., Kato, K., Kaneko, F., and Phanichphant, S.: Controlling surface plasmon optical transmission with an electrochemical switch using conducting polymer thin films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 22, 4383 (2012).Google Scholar
10.Janmanee, R., Baba, A., Phanichphant, S., Sriwichai, S., Shinbo, K., Kato, K., and Kaneko, F.: In situ electrochemical-transmission surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy for poly(pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid) thin film-based biosensor applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4, 4270 (2012).Google Scholar
11.Lertvachirapaiboon, C., Supunyabut, C., Baba, A., Ekgasit, S., Thammacharoen, C., Shinbo, K., Kato, K., and Kaneko, F.: Transmission surface plasmon resonance signal enhancement via growth of gold nanoparticles on a gold grating surface. Plasmonics 8, 369 (2013).Google Scholar
12.Lertvachirapaiboon, C., Baba, A., Ekgasit, S., Thammacharoen, C., Shinbo, K., Kato, K., and Kaneko, F.: Distance-dependent surface plasmon resonance coupling between a gold grating surface and silver nanoparticles. Plasmonics 9, 899 (2014).Google Scholar
13.Lertvachirapaiboon, C., Baba, A., Ekgasit, S., Shinbo, K., Kato, K., and Kaneko, F.: Transmission surface plasmon resonance imaging of silver nanoprisms enhanced propagating surface plasmon resonance on a metallic grating structure. Sens. Actuators B 249, 39 (2017).Google Scholar
14.Maurer, T., Nicolas, R., Lévêque, G., Subramanian, P., Proust, J., Béal, J., Schuermans, S., Vilcot, J.P., Herro, Z., Kazan, M., Plain, J., Boukherroub, R., Akjouj, A., Djafari-Rouhani, B., Adam, P.M., and Szunerits, S.: Enhancing LSPR sensitivity of Au gratings through graphene coupling to Au film. Plasmonics 9, 507 (2014).Google Scholar
15.Thio, T., Ghaemi, H.F., Lezec, H.J., Wolff, P.A., and Ebbesen, T.W.: Surface-plasmon-enhanced transmission through hole arrays in Cr films. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 16, 1743 (1999).Google Scholar
16.Brolo, A.G., Gordon, R., Leathem, B., and Kavanagh, K.L.: Surface plasmon sensor based on the enhanced light transmission through arrays of nanoholes in gold films. Langmuir 20, 4813 (2004).Google Scholar
17.Gordon, R., Sinton, D., Kavangh, K.L., and Brolo, A.G.: A new generation of sensors based on extraordinary optical transmission. Acc. Chem. Res. 41, 1049 (2008).Google Scholar
18.Im, H., Lesuffleur, A., Lindquist, N.C., and Oh, S.H.: Plasmonic nanoholes in a multichannel microarray format for parallel kinetic assays and differential sensing. Anal. Chem. 81, 2854 (2009).Google Scholar
19.Im, H., Lee, S.H., Wittenberg, N.J., Johnson, T.W., Lindquist, N.C., Nagpal, P., Norris, D.J., and Oh, S.H.: Template-stripped smooth Ag nanohole arrays with silica shells for surface plasmon resonance biosensing. ACS Nano 5, 6244 (2011).Google Scholar
20.Escobedo, C.: On-chip nanohole array based sensing: a review. Lab. Chip 13, 2445 (2013).Google Scholar
21.Wang, Y., Wu, L., Zhou, X., Wong, T.I., Zhang, J., Bai, P., Li, E.P., and Liedberg, B.: Incident-angle dependence of fluorescence enhancement and biomarker immunoassay on gold nanohole array. Sens. Actuators B 186, 205 (2013).Google Scholar
22.Song, H.Y., Wong, T.I., Guo, S., Deng, J., Tan, C., Gorelik, S., and Zhou, X.: Nanoimprinted thrombin aptasensor with picomolar sensitivity based on plasmon excited quantum dots. Sens. Actuators B 221, 207 (2015).Google Scholar
23.Barik, A., Otto, L.M., Yoo, D., Jose, J., Johnson, T.W., and Oh, S.H.: Dielectrophoresis-enhanced plasmonic sensing with gold nanohole arrays. Nano Lett. 14, 2006 (2014).Google Scholar
24.Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Wong, T.I., Liu, X., Zhou, X., and Liedberg, B.: Electrofocusing-enhanced localized surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Nanoscale 7, 17244 (2015).Google Scholar
25.Cetin, A.E., Coskun, A.F., Galarreta, B.C., Huang, M., Herman, D., Ozcan, A., and Altug, H.: Handheld high-throughput plasmonic biosensor using computation on-chip imaging. Light Sci. Appl. 3, e122 (2014).Google Scholar
26.Lee, K.L., You, M.L., Tsai, C.H., Lin, E.H., Hsieh, S.Y., Ho, M.H., Hsu, J.C., and Wei, P.K.: Nanoplasmonic biochips for rapid label-free detection of imdacloprid pesticides with a smartphone. Biosens. Bioelectron. 75, 88 (2016).Google Scholar
27.Wang, X., Chang, T., Lin, G., Gartia, M.R., and Liu, G.L.: Self-referenced smartphone-based nanoplasmonic imaging platform for colorimetric biochemical sensing. Anal. Chem. 89, 611 (2017).Google Scholar
28.Baba, A., Kanda, K., Ohno, T., Ohdaira, Y., Shinbo, K., Kato, K., and Kaneko, F.: Multimode surface plasmon excitations on organic thin film/metallic diffraction grating. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 49, 01AE02 (2010).Google Scholar
29.Lertvachirapaiboon, C., Yamazaki, R., Pienpinijtham, P., Baba, A., Ekgasit, S., Thammacharoen, C., Shinbo, K., Kato, K., and Kaneko, F.: Solution-based fabrication of gold grating film for use as a surface plasmon resonance sensor chip. Sens. Actuators B 173, 316 (2012).Google Scholar
30.Lertvachirapaiboon, C., Baba, A., Ekgasit, S., Shinbo, K., Kato, K., and Kaneko, F.: Microfluidic transmission surface plasmon resonance enhancement for biosensor applications. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 56, 017002 (2017).Google Scholar
31.Shinbo, K., Takizawa, K., Obata, N., Lertvachirapaiboon, C., Baba, A., Kato, K., and Kaneko, F.: Transmission light property due to grating-coupled long-range surface plasmon resonance. Polym. Bull. 73, 2539 (2016).Google Scholar
32.Hassan, S., Khodami, M., Tait, R.N., and Berini, P.: Fabrication of long-range surface plasmon-polariton Bragg gratings with microfluidic channels in Cytop claddings. Microelectron. Eng. 135, 38 (2015).Google Scholar
33.Fogg, E.T., Hixson, A.N., and Thompson, A.R.: Density and refractive indexes for ethylene glycol-water solutions. Anal. Chem. 27, 1609 (1955).Google Scholar
- 13
- Cited by


