Article contents
Photoelectrochemical response of Fe2O3 films reinforced with BiFeO3 nanofibers
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 June 2018
Abstract
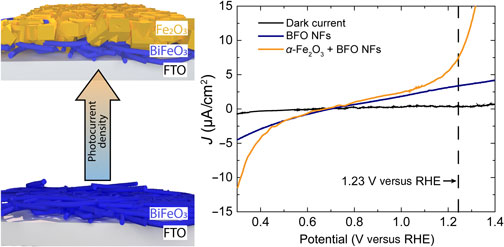
BiFeO3 (BFO) p-type semiconducting nanofibers were deposited on fluorine-doped SnO2 substrates by a combination of electrospinning (BiFeO3) and spin-coating (Fe2O3) procedures. Photocurrent density values of BFO nanofibers which increased with the annealing temperature to values six times larger were obtained. Different amounts of BFO nanofibers (5, 10, and 25 wt%) were also integrated into α-Fe2O3 films. The photocurrent density of the α-Fe2O3/BFO nanofiber films had the highest value for a 10 wt% BFO nanofibers. The anisotropy in charge transport due to the underlying nanofibrous pathways which prevented the charge carrier recombination was the main cause for the enhancement of the photocurrent density.
Information
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2018
References
- 5
- Cited by


