Article contents
On-the-fly segmentation approaches for x-ray diffraction datasets for metallic glasses
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 30 August 2017
Abstract
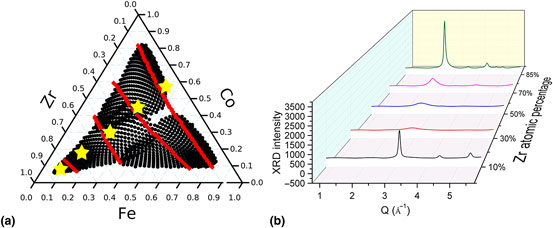
Investment in brighter sources and larger detectors has resulted in an explosive rise in the data collected at synchrotron facilities. Currently, human experts extract scientific information from these data, but they cannot keep pace with the rate of data collection. Here, we present three on-the-fly approaches—attribute extraction, nearest-neighbor distance, and cluster analysis—to quickly segment x-ray diffraction (XRD) data into groups with similar XRD profiles. An expert can then analyze representative spectra from each group in detail with much reduced time, but without loss of scientific insights. On-the-fly segmentation would, therefore, result in accelerated scientific productivity.
Information
- Type
- Research Letters
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2017
Footnotes
These authors contributed equally to this work.
References
- 1
- Cited by

