No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 March 2018
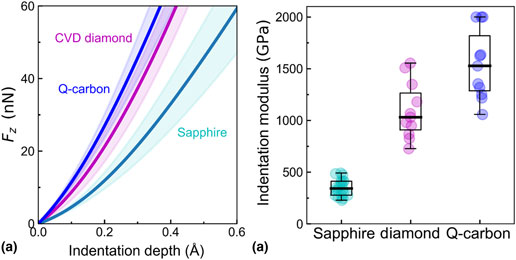
A new phase of carbon named Q-carbon is found to be over 40% harder than diamond. This phase is formed by nanosecond laser melting of amorphous carbon and rapid quenching from the super-undercooled state. Closely packed atoms in molten metallic carbon are quenched into Q-carbon with 80–85% sp3 and the rest sp2. The number density of atoms in Q-carbon can vary from 40% to 60% higher than diamond cubic lattice, as the tetrahedra packing efficiency increases from 70% to 80%. Using this semiempirical approach, the corresponding increase in Q-carbon hardness is estimated to vary from 48% to 70% compared to diamond.