Article contents
Architected mechanical designs in tissue engineering
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 August 2020
Abstract
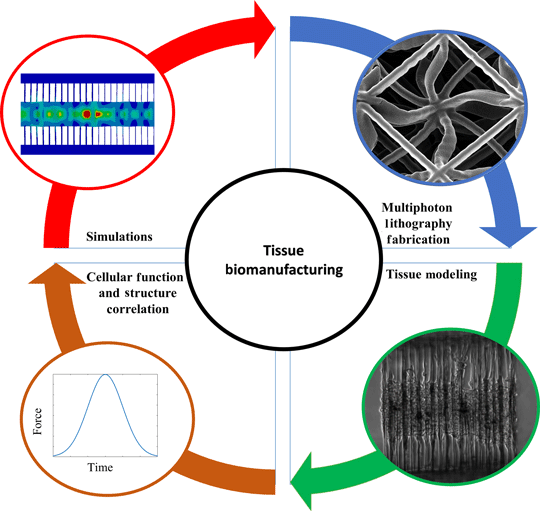
The deeper comprehension of biological phenomena has led to the pursuit of designing and architecting complex biological systems. This has been incorporated through the advances in bioprinting of artificial organs and implants even at the microscale. In addition, tissue modeling has been employed to understand and prevent malfunctional and detrimental mechanisms that lead to fatal diseases. Furthermore, the endeavor to convey the mechanical properties of both scaffolds and cells has enabled the unveiling of disease modeling and regenerative medicine. This paper aims to provide a brief review of the design, modeling and characterization of conventional and architected structures employed in bioengineering.
Information
- Type
- Prospective Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society, 2020
References
- 4
- Cited by


