Article contents
Time-dependent Landau theory for order/disorder processes in minerals
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 July 2018
Abstract
Recent advances in the use of time-dependent order parameter theory to describe the kinetics of order/disorder transitions are reviewed. The time dependence of a macroscopic order parameter, Q, follows, to a good approximation:
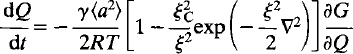
For systems in which the order parameter has a long correlation length (large ξ) and is not conserved (small ξC), the Ginzburg-Landau equation provides a general kinetic solution:
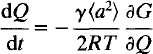
Specific rate laws can be derived from this general solution depending on whether the crystals remain homogeneous with respect to the order parameter, Q. The advantages of the overall approach are, firstly, that it does not depend on the detailed structure of the material being examined; secondly, that the order parameter can be followed experimentally through its relationship with other properties, such as spontaneous strain, excess entropy, intensities of superlattice reflections, etc.; and, finally, that conventional Landau expansions in Q may be used to describe the thermodynamic driving forces.
For a simple second-order transition in crystals which remain homogeneous in Q the rate law is:
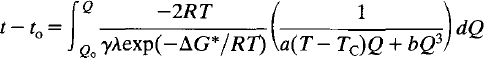
If the free energy of activation varies with the state of order of the crystal, this becomes:
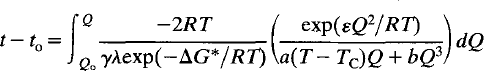
Simplifying assumptions can be introduced into the mathematics, or the integrals can be solved numerically. For crystals which remain homogeneous, the simplest solution valid only over small deviations from equilibrium is:
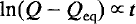
For crystals which develop heterogeneities in Q, the rate laws change significantly and we find as an extreme case:
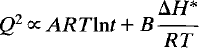
where the A coefficient may be temperature dependent.
Experimental data available for a limited number of minerals (omphacite, anorthite, albite, cordierite and nepheline) are used to demonstrate the practical implications of the overall approach. As anticipated from the theory, modulated structures commonly develop during kinetic experiments, the observed rate laws depend on whether the critical point of the ordering is located at the centre or boundary of the Brillouin zone, and the rate laws for ordering and disordering can be quite different. The importance of different length scales, not only in the different techniques for characterizing states of order (IR, NMR, calorimetry, X-ray diffraction, etc.) but also for interpreting observed mechanisms and rate laws, is also outlined.
Use of the order parameter in Landau expansions and in Ginzburg-Landau rate laws provides, in principle, a means of predicting the equilibrium and non-equilibrium evolution of minerals in nature.
Information
- Type
- Mineralogy
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland 1989
References
- 34
- Cited by

