No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
RANDOMNESS NOTIONS AND REVERSE MATHEMATICS
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 09 September 2019
Abstract
We investigate the strength of a randomness notion 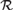 ${\cal R}$ as a set-existence principle in second-order arithmetic: for each Z there is an X that is
${\cal R}$ as a set-existence principle in second-order arithmetic: for each Z there is an X that is 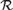 ${\cal R}$-random relative to Z. We show that the equivalence between 2-randomness and being infinitely often C-incompressible is provable in
${\cal R}$-random relative to Z. We show that the equivalence between 2-randomness and being infinitely often C-incompressible is provable in 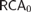 $RC{A_0}$. We verify that
$RC{A_0}$. We verify that  $RC{A_0}$ proves the basic implications among randomness notions: 2-random
$RC{A_0}$ proves the basic implications among randomness notions: 2-random 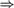 $\Rightarrow$ weakly 2-random
$\Rightarrow$ weakly 2-random 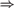 $\Rightarrow$ Martin-Löf random
$\Rightarrow$ Martin-Löf random 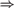 $\Rightarrow$ computably random
$\Rightarrow$ computably random  $\Rightarrow$ Schnorr random. Also, over
$\Rightarrow$ Schnorr random. Also, over 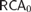 $RC{A_0}$ the existence of computable randoms is equivalent to the existence of Schnorr randoms. We show that the existence of balanced randoms is equivalent to the existence of Martin-Löf randoms, and we describe a sense in which this result is nearly optimal.
$RC{A_0}$ the existence of computable randoms is equivalent to the existence of Schnorr randoms. We show that the existence of balanced randoms is equivalent to the existence of Martin-Löf randoms, and we describe a sense in which this result is nearly optimal.
Keywords
Information
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Association for Symbolic Logic 2019

