Article contents
Overstability of plasma slow electron holes
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 28 February 2022
Abstract
Sufficient conditions are found on the ion velocity distribution 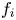 $f_i$ and potential amplitude for stability of steady electron holes moving at slow speeds, coinciding with the bulk of
$f_i$ and potential amplitude for stability of steady electron holes moving at slow speeds, coinciding with the bulk of 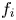 $f_i$. Fully establishing stability requires calculation of the ion response to shift potential perturbations having an entire range of oscillatory frequencies, because under some conditions real frequencies intermediate between the ion and electron responses prove to be unstable even when the extremes are not. The mechanism of this overstability is explained and calculated in detail. Electron holes of peak potential
$f_i$. Fully establishing stability requires calculation of the ion response to shift potential perturbations having an entire range of oscillatory frequencies, because under some conditions real frequencies intermediate between the ion and electron responses prove to be unstable even when the extremes are not. The mechanism of this overstability is explained and calculated in detail. Electron holes of peak potential 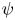 $\psi$ less than approximately 0.01 times the background temperature (
$\psi$ less than approximately 0.01 times the background temperature (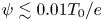 $\psi \lesssim 0.01T_0/e$) avoid the oscillatory instability entirely. For them, the necessary condition that there be a local minimum in
$\psi \lesssim 0.01T_0/e$) avoid the oscillatory instability entirely. For them, the necessary condition that there be a local minimum in 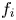 $f_i$ in which the hole resides is also sufficient, unless the magnetic field
$f_i$ in which the hole resides is also sufficient, unless the magnetic field 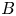 $B$ is low enough to permit the transverse instability having finite wavenumber
$B$ is low enough to permit the transverse instability having finite wavenumber 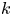 $k$ perpendicular to
$k$ perpendicular to 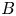 $B$.
$B$.
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2022. Published by Cambridge University Press
References
REFERENCES
- 4
- Cited by


