Article contents
Multidimensional SPM applied for nanoscale conductance mapping
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 December 2013
Abstract
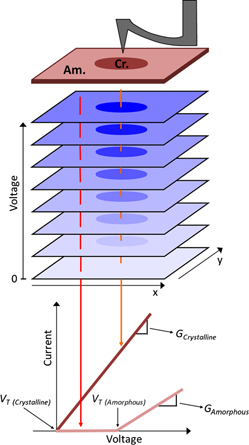
A new approach has been developed for nanoscale conductance mapping (NCM) based on multidimensional atomic force microscopy (AFM) to efficiently investigate the nanoscale electronic properties of heterogeneous surfaces. The technique uses a sequence of conductive AFM images, all acquired in a single area but each with incrementally higher applied voltages. This generates a matrix of current versus voltage (I–V) spectra, providing nanoscale maps of conductance and current nonlinearities with negligible spatial drift. For crystalline and amorphous phases of a GeSe chalcogenide phase change film, conductance and characteristic amorphous phase “turn-on” voltages are mapped with results providing traditional point-by-point I–V measurements, but acquired hundreds of times faster. Although similar to current imaging tunneling spectroscopy in a scanning tunneling microscope, the NCM technique does not require conducting specimens. It is therefore a promising approach for efficient, quantitative electronic investigations of heterogeneous materials used in sensors, resistive memories, and photovoltaics.
Keywords
Information
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2013
References
REFERENCES
- 8
- Cited by

