Article contents
Largely enhanced thermoelectric properties of the binary-phased PbTe–Sb2Te3 nanocomposites
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 January 2012
Abstract
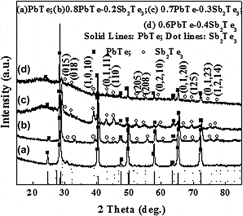
In this article, the binary-phased PbTe–Sb2Te3 nanopowders were synthesized via a hydro/solvo-thermal route to improve the thermoelectric properties of PbTe matrix material. The single-phased PbTe powders exhibit pure nanoparticles, but the binary-phased PbTe–Sb2Te3 powders have a mixed morphology composed of nanospheres and nanoribbons. Our results suggest that the thermal conductivity of the binary-phased PbTe–Sb2Te3 bulks can be reduced significantly and the Seebeck coefficient can be increased obviously, although the electrical conductivity can also be decreased sharply. Consequently, a large figure of merit 0.85 at 623 K can be achieved for 0.7PbTe–0.3Sb2Te3 bulk, which is enhanced by about one time as compared to that of the single-phased PbTe bulk. This large enhancement could be attributed to the lowered carrier concentration and the increased interface scattering in the binary-phased PbTe–Sb2Te3 materials with a mixed morphology.
Information
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2012
References
REFERENCES
- 7
- Cited by

